Pancreatic cancer mortality trend in Montenegro, 1990-2018
- PMID: 40800671
- PMCID: PMC12342969
- DOI: 10.1093/gastro/goaf076
Pancreatic cancer mortality trend in Montenegro, 1990-2018
Abstract
Background: According to the Global Cancer Observatory 2020 report, pancreatic cancer occupies the 11th position among the leading causes of cancer-related mortality in both sexes, with nearly 500,000 deaths annually worldwide. This study aimed to evaluate the trend of mortality due to pancreatic cancer in Montenegro from 1990 to 2018 and to contribute to the effective planning of preventive strategies for pancreatic cancer as well as future health policies and initiatives.
Methods: We utilized national data on the causes of death from pancreatic cancer and codes 157 from the 9th and C25 from the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases. The trend was described by using Joinpoint, Poisson, and linear regression.
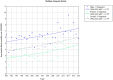
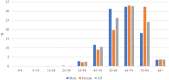
Results: Mortality rates of pancreatic cancer in Montenegro consistently increased (P < 0.05) for the overall level for both men and women, with the average annual percentage change (AAPC) in the AAPC order (95% confidence interval): 1.7% (0.9%-2.5%) overall, 1.3% (0.4%-2.1%) in men, and 2.2% (0.9%-3.5%) in women. The majority of those who died from pancreatic cancer were aged 65-74 years (32.7%), 55-64 years (26.3%), and 75-84 years (24.1%).
Conclusions: The persistent increase in pancreatic cancer mortality rates in Montenegro, observed in both men and women, highlights a concerning public health trend. With the highest proportion of deaths occurring among individuals aged 55-84 years, these findings underscore the urgent need for policymakers to implement a national strategy targeting early detection, prevention, and improved management, especially among the most affected age groups.
Keywords: Montenegro; mortality; pancreatic cancer; trend.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press and Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Lok V, Ngai CH et al. worldwide burden of, risk factors for, and trends in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2021;160:744–54. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2017 Pancreatic Cancer Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of pancreatic cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:934–47. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

