Turning Polluted Biomass Waste into Sustainable Carbon-Based Catalysts for Hydrogen Production via Water Electrolysis
- PMID: 40800712
- PMCID: PMC12337815
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.5c02282
Turning Polluted Biomass Waste into Sustainable Carbon-Based Catalysts for Hydrogen Production via Water Electrolysis
Abstract
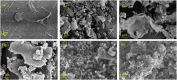
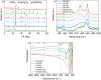
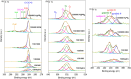
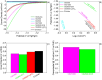
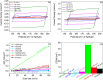
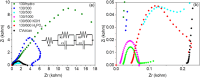
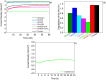
The development of highly efficient, effective, and low-cost carbon-based catalysts for hydrogen production through water electrolysis represents a significant challenge in sustainable energy conversion. In this work, carbon materials derived from biomass waste, specifically a metal-polluted vegetal species () from a former mining location, were used. Biomass was subjected to hydrothermal carbonization, producing hydrochar. The influence of both thermal and chemical post-treatment was studied in relation to hydrogen production efficiency. The thermal treatment was conducted at 300, 500, and 1000 °C, while the chemical precursors used were KOH and H3PO4. Additionally, these waste-derived carbon materials were compared with carbon Vulcan XC-72, a common reference material in these processes originated from fossil sources. Several electrochemical techniques were employed to evaluate and identify the most suitable sample for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). Additionally, physicochemical characterization analyses were conducted to gain a comprehensive understanding of the morphology, composition, and surface structure of the biomass-derived carbon materials, as well as to establish correlations with their electrochemical behavior toward the HER. The sample that demonstrated the most favorable performance was the one chemically activated with KOH, which exhibited an outstanding Tafel slope (147 mV/dec) and a low overpotential at 10 mA/cm2 (-550 mV vs RHE) surpassing even the commercial Vulcan XC-72 sample. Furthermore, the chronoamperometry test showed a very stable performance for this sample. These results demonstrate that plant biomass waste containing metals presents a viable alternative to carbon blacks, commonly used as electrocatalysts for hydrogen production, also providing an efficient and sustainable method to valorize these wastes.
© 2025 American Chemical Society.
Figures
References
-
- Liu Z., Zhou Q., Zhao B., Li S., Xiong Y., Xu W.. Few-layer N-doped porous carbon nanosheets derived from corn stalks as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Fuel. 2020;280:118567. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118567. - DOI
-
- Jamesh M. I., Sun X.. Recent progress on earth abundant electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction (OER) in alkaline medium to achieve efficient water splitting – A review. J. Power Sources. 2018;400:31–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.07.125. - DOI
-
- Guo T., Zhang X., Liu T., Wu Z., Wang D.. N, K Co-activated biochar-derived molybdenum carbide as efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020;509:144879. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144879. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
