The Role of Nuclear Phosphoinositides in the p53-MDM2 Nexus
- PMID: 40801560
- PMCID: PMC12346208
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14151126
The Role of Nuclear Phosphoinositides in the p53-MDM2 Nexus
Abstract
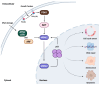
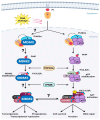
Recent insights into the p53-MDM2 nexus have advanced deeper understanding of their regulation and potent impact on cancer heterogeneity. The roles of nuclear phosphoinositide (PIPns) in modulating this pathway are emerging as a key mechanism. Here, we dissect the molecular mechanisms by which nuclear PIPns stabilize p53 through the recruitment of small heat shock proteins (sHSPs), activate the nuclear phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT signaling cascade, and modulate MDM2 function to regulate the p53-MDM2 interaction. We propose potential mechanisms by which nuclear PIPns coordinate signaling with nuclear p53, AKT, and MDM2. Ultimately, we highlight that nuclear PIPns serve as a 'third messenger' within the p53-MDM2 axis, expanding the current framework of non-canonical nuclear signaling in cancer biology.
Keywords: AKT; MDM2; nucleus; p53; phosphoinositide; small heat shock protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EVA1A reverses lenvatinib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating PI3K/AKT/p53 signaling axis.Apoptosis. 2024 Aug;29(7-8):1161-1184. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01967-0. Epub 2024 May 14. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38743191
-
Regulation of the MDM2-p53 nexus by a nuclear phosphoinositide and small heat shock protein complex.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jul 26;301(9):110527. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110527. Online ahead of print. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40721017 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MDM2-p53 Nexus by a Nuclear Phosphoinositide and Small Heat Shock Protein Complex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 17:2025.04.11.648454. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.11.648454. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Biol Chem. 2025 Jul 26;301(9):110527. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110527. PMID: 40406464 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Canonical and non-canonical functions of p53 isoforms: potentiating the complexity of tumor development and therapy resistance.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jun 12;15(6):412. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06783-7. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38866752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The nuclear phosphoinositide response to stress.Cell Cycle. 2020 Feb;19(3):268-289. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1711316. Epub 2020 Jan 5. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 31902273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

