From Development to Regeneration: Insights into Flight Muscle Adaptations from Bat Muscle Cell Lines
- PMID: 40801622
- PMCID: PMC12346413
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14151190
From Development to Regeneration: Insights into Flight Muscle Adaptations from Bat Muscle Cell Lines
Abstract
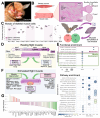
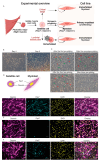
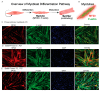
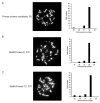
Skeletal muscle regeneration depends on muscle stem cells, which give rise to myoblasts that drive muscle growth, repair, and maintenance. In bats-the only mammals capable of powered flight-these processes must also sustain contractile performance under extreme mechanical and metabolic stress. However, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying bat muscle physiology remain largely unknown. To enable mechanistic investigation of these traits, we established the first myoblast cell lines from the pectoralis muscle of Pteronotus mesoamericanus, a highly maneuverable aerial insectivore. Using both spontaneous immortalization and exogenous hTERT/CDK4 gene overexpression, we generated two stable cell lines that retain proliferative capacity and differentiate into contractile myotubes. These cells exhibit frequent spontaneous contractions, suggesting robust functional integrity at the neuromuscular junction. In parallel, we performed transcriptomic and metabolic profiling of native pectoralis tissue in the closely related Pteronotus parnellii to define molecular programs supporting muscle specialization. Gene expression analyses revealed enriched pathways for muscle metabolism, development, and regeneration, highlighting supporting roles in tissue maintenance and repair. Consistent with this profile, the flight muscle is triglyceride-rich, which serves as an important fuel source for energetically demanding processes, including muscle contraction and cellular recovery. Integration of transcriptomic and metabolic data identified three key metabolic modules-glucose utilization, lipid handling, and nutrient signaling-that likely coordinate ATP production and support metabolic flexibility. Together, these complementary tools and datasets provide the first in vitro platform for investigating bat muscle research, enabling direct exploration of muscle regeneration, metabolic resilience, and evolutionary physiology.
Keywords: CDK4; bat; flight muscle biology; hTERT; myoblast cell line; myotube; proliferation and differentiation; regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Update of
-
From Development to Regeneration: Insights into Flight Muscle Adaptations from Bat Muscle Cell Lines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 3:2025.07.01.662643. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.01.662643. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cells. 2025 Aug 01;14(15):1190. doi: 10.3390/cells14151190. PMID: 40631317 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
From Development to Regeneration: Insights into Flight Muscle Adaptations from Bat Muscle Cell Lines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 3:2025.07.01.662643. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.01.662643. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cells. 2025 Aug 01;14(15):1190. doi: 10.3390/cells14151190. PMID: 40631317 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

