Oxy210 Inhibits Hepatic Expression of Senescence-Associated, Pro-Fibrotic, and Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Mice During Development of MASH and in Hepatocytes In Vitro
- PMID: 40801623
- PMCID: PMC12346697
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14151191
Oxy210 Inhibits Hepatic Expression of Senescence-Associated, Pro-Fibrotic, and Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Mice During Development of MASH and in Hepatocytes In Vitro
Abstract
Background: Senescence, a state of permanent cell cycle arrest, is a complex cellular phenomenon closely affiliated with age-related diseases and pathological fibrosis. Cellular senescence is now recognized as a significant contributor to organ fibrosis, largely driven by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling, such as in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and myocardial fibrosis, which can lead to heart failure, cystic fibrosis, and fibrosis in pancreatic tumors, to name a few. MASH is a progressive inflammatory and fibrotic liver condition that has reached pandemic proportions, now considered the largest non-viral contributor to the need for liver transplantation.
Methods: We previously studied Oxy210, an anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory, orally bioavailable, oxysterol-based drug candidate for MASH, using APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice, a humanized hyperlipidemic mouse model that closely recapitulates the hallmarks of human MASH. In this model, treatment of mice with Oxy210 for 16 weeks caused significant amelioration of the disease, evidenced by reduced hepatic inflammation, lipid deposition, and fibrosis, atherosclerosis and adipose tissue inflammation.
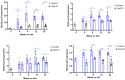
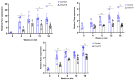
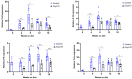
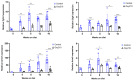
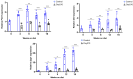
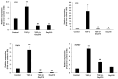
Results: Here we demonstrate increased hepatic expression of senescence-associated genes and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), correlated with the expression of pro-fibrotic and pro-inflammatorygenes in these mice during the development of MASH that are significantly inhibited by Oxy210. Using the HepG2 human hepatocyte cell line, we demonstrate the induced expression of senescent-associated genes and SASP by TGF-β and inhibition by Oxy210.
Conclusions: These findings further support the potential therapeutic effects of Oxy210 mediated in part through inhibition of senescence-driven hepatic fibrosis and inflammation in MASH and perhaps in other senescence-associated fibrotic diseases.
Keywords: MASH; Oxy210; fibrosis; oxysterols; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
F.P., F.S. and F.W. are employees and hold shares in MAX BioPharma, Inc., a company with a commercial interest in drug discovery and development. Beyond that, these authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

