Characterizations of Electrospun PVDF-Based Mixed Matrix Membranes with Nanomaterial Additives
- PMID: 40801691
- PMCID: PMC12348061
- DOI: 10.3390/nano15151151
Characterizations of Electrospun PVDF-Based Mixed Matrix Membranes with Nanomaterial Additives
Abstract
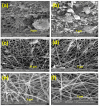
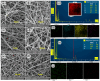
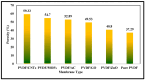
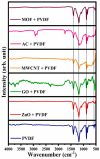
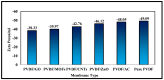
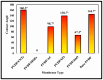
Water scarcity poses a formidable challenge around the world, especially in arid regions where limited availability of freshwater resources threatens both human well-being and ecosystem sustainability. Membrane-based desalination technologies offer a viable solution to address this issue by providing access to clean water. This work ultimately aims to develop a novel permselective polymeric membrane material to be employed in an electrochemical desalination system. This part of the study addresses the optimization, preparation, and characterization of a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) polymeric membrane using the electrospinning technique. The membranes produced in this work were fabricated under specific operational, environmental, and material parameters. Five different additives and nano-additives, i.e., graphene oxide (GO), carbon nanotubes (CNTs), zinc oxide (ZnO), activated carbon (AC), and a zeolitic imidazolate metal-organic framework (ZIF-8), were used to modify the functionality and selectivity of the prepared PVDF membranes. Each membrane was synthesized at two different levels of additive composition, i.e., 0.18 wt.% and 0.45 wt.% of the entire PVDF polymeric solution. The physiochemical properties of the prepared membranes were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), zeta potential, contact angle, conductivity, porosity, and pore size distribution. Based on findings of this study, PVDF/GO membrane exhibited superior results, with an electrical conductivity of 5.611 mS/cm, an average pore size of 2.086 µm, and a surface charge of -38.33 mV.
Keywords: PVDF; electrospinning; metal–organic frameworks; nano-additives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shokri A., Sanavi Fard M. A sustainable approach in water desalination with the integration of renewable energy sources: Environmental engineering challenges and perspectives. Environ. Adv. 2022;9:100281. doi: 10.1016/j.envadv.2022.100281. - DOI
-
- Lalia B.S., Kochkodan V., Hashaikeh R., Hilal N. A review on membrane fabrication: Structure, properties and performance relationship. Desalination. 2013;326:77–95. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2013.06.016. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

