Schiff Base-Functionalized Melamine Sponge with Hierarchical Porous Architecture for High-Efficiency Removal of Organic Dyes in Wastewater
- PMID: 40801697
- PMCID: PMC12348324
- DOI: 10.3390/nano15151157
Schiff Base-Functionalized Melamine Sponge with Hierarchical Porous Architecture for High-Efficiency Removal of Organic Dyes in Wastewater
Abstract
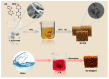
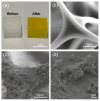
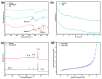
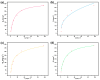
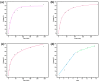
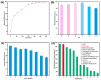
Melamine sponges have demonstrated significant application potential in the field of adsorption materials due to their unique three-dimensional porous network structure, excellent chemical/mechanical stability, and abundant amino active sites on the surface. However, the development of modified melamine sponges with efficient Congo red dye removal capabilities remains a substantial challenge. In this study, a stable linear polymer network structure was constructed on the surface of melamine sponges via an in situ polymerization strategy based on the Schiff base reaction mechanism. Characterization analyses reveal that the modified sponge not only retained the original porous skeleton structure but also significantly enhanced the density of surface active sites. Experimental data demonstrate that the modified sponge exhibited excellent adsorption performance for Congo red dye, with the adsorption process conforming to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and achieving a practical maximum adsorption capacity of 380.4 mg/g. Notably, the material also displayed favorable cyclic stability. This study provides an efficient adsorbent for Congo red dye-contaminated wastewater treatment through the development of a novel surface-functionalized sponge material while also offering new solutions for advancing the practical applications of melamine-based porous materials and environmental remediation technologies.
Keywords: Congo red dye; absorption; composite foam; melamine foam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Du X., Nie H., Qu Y., Jia H., Liu Y., Yin B. Revisiting the Efficacy of COF Treatment for Dyes in Wastewater: A Comprehensive Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025;13:115660. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2025.115660. - DOI
-
- Al-Sakkaf M.K., Basfer I., Iddrisu M., Bahadi S.A., Nasser M.S., Abussaud B., Drmosh Q.A., Onaizi S.A. An Up-to-Date Review on the Remediation of Dyes and Phenolic Compounds from Wastewaters Using Enzymes Immobilized on Emerging and Nanostructured Materials: Promises and Challenges. Nanomaterials. 2023;13:2152. doi: 10.3390/nano13152152. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qu Y., Liu Y., Jia H., Xu S., Zhang M., Xiao T., Du X. Preparation of Self-Standing Ultra-Thin Three-Dimensional Covalent Organic Frameworks by Interfacial Polymerization for Dye Separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024;12:112711. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.112711. - DOI
-
- Qu Y., Zha Y., Du X., Xu S., Zhang M., Xu L., Jia H. Interfacial Polymerization of Self-Standing Covalent Organic Framework Membranes at Alkane/Ionic Liquid Interfaces for Dye Separation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022;4:7528–7536. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.2c01209. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

