Viloxazine Extended-Release Capsules in Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Results of a Long-Term, Phase 3, Open-Label Extension Trial
- PMID: 40802027
- PMCID: PMC12515214
- DOI: 10.1007/s40263-025-01209-0
Viloxazine Extended-Release Capsules in Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Results of a Long-Term, Phase 3, Open-Label Extension Trial
Abstract
Background and objective: Viloxazine ER (extended-release capsules; Qelbree®) is a nonstimulant medication that has been approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of pediatric and adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). This phase 3, open-label extension (OLE) trial evaluated the long-term safety and efficacy of viloxazine ER in children and adolescents with ADHD.
Methods: Participants completing the phase 2 or one of the four phase 3 double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials were eligible for the OLE trial. Upon entering the OLE, double-blind treatment was discontinued and participants were administered viloxazine ER 100 mg/day (children, aged 6-11 years) or 200 mg/day, (adolescents, aged 12-18 years), with dosage titration as needed over a 12-week dose-optimization period (up to 400 mg/day [children] or 600 mg/day [adolescents]). Participants then entered a maintenance period that continued through US FDA-approval (up to 72 months). Safety (primary objective) was assessed relative to OLE baseline using adverse event (AE), clinical laboratory tests, vital sign, ECG, and Columbia Suicide Severity-Rating Scale (C-SSRS) monitoring. Efficacy was assessed relative to double-blind baseline using the ADHD Rating Scale (ADHD-RS-IV/5) and the Clinical Global Impression-Improvement (CGI-I) scale. Study visits for these assessments occurred every ~ 3 months throughout maintenance treatment.
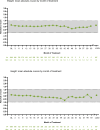
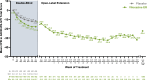
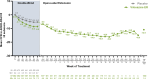
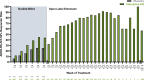
Results: Participants (N = 1100) included 646 children and 454 adolescents (66.5% male/33.5% female). Median (range) exposure to viloxazine ER in the OLE was 260 (1-1896) days, and the median modal (most frequently used) viloxazine ER doses were 300 mg/day for children and 400 mg/day for adolescents. AEs included (≥ 5% incidence) nasopharyngitis (9.7%), somnolence (9.5%), headache (8.9%), decreased appetite (6.0%), and fatigue (5.7%). AEs were mostly mild or moderate in severity (3.9% reported any severe AE); AEs led to discontinuation in 8.2% of participants. The mean ± SD changes from double-blind baseline in ADHD-RS IV/5 total score were -24.3 ± 12.0 at Month 3, -26.1 ± 11.5 at Month 12, and -22.4 ± 13.6 at participants' last OLE study visit.
Conclusions: The results of this large-scale safety trial support the long-term use of viloxazine ER as a generally well-tolerated and effective treatment option for pediatric ADHD. No new safety concerns emerged, and efficacy results suggest the potential for continued improvement over that seen during double-blind treatment.
Clinical trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT02736656.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Funding: This work and its open access publication were funded by Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Conflicts of Interest: R.L.F. receives or has received research support, acted as a consultant and/or has received honoraria from Abbvie, Ajna, Akili, American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, American Psychiatric Press, Bioprojet, BioXcel, Bristol Myers Squibb,Corium, Elsevier, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Iqvia, Karuna, Lundbeck, Maplight, Merck, MJH Life Sciences, NIH, Novartis, Otsuka, Oxford University Press, PaxMedica, PCORI, Pfizer, Radius, Sage, Signant Health, Sumitomo Pharma, Sunovion, Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Takeda, Tris, Viatris, and Xenon. Over the past 3 years, J.W. has received research support from Supernus and served as a consultant for Iron Shore and Adlon Pharmaceuticals. M.L. is a consultant for Vistagen Therapeutics and Newleos Pharma, and in the past 3 years has conducted clinical trials for Supernus, Alto, Biohaven, Janssen, Otsuka, Compass, Abbvie, and Relmada. A.K. has received honoraria from Supernus and in the past 3 years has conducted clinical research for Abbvie, Axsome, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cingulate, Corium, Janssen, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relmada, and Supernus. N.F., P.Q., I.Y., Z.M-C., V.R.L., and J.R. are employees of Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Ethics Approval: The trial was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) Good Clinical Practice Guidelines for biomedical research, and the United States (US) Code of Federal Regulations (21 CFR). The central IRB (Advarra) approved the trial protocol under Pro00026366. Consent to Participate: Each participant’s parent or legal guardian signed an informed consent form (ICF); participants signed an informed assent form, and those turning 18 years of age during the trial also signed an ICF. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Availability of Data and Materials: The data are not available in a repository, but data will be made available upon reasonable request directed to jrubin@supernus.com. Code Availability: Not applicable. Author Contributions: Conceptualization and design: R.L.F. Methodology and data collection: R.L.F., J.W., A.K., N.F., and M.L. Analysis and interpretation: R.L.F., J.W., I.Y., Z.M.C., V.R.L., P.Q., and J.R. Writing, review, and editing: R.L.F., M.L., J.W., I.Y., Z.M.C., V.R.L., P.Q., and J.R. All authors read and approved the final submitted manuscript and agree to be accountable for this work.
Figures



References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Arlington: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

