Relationship between scoring systems and inflammatory parameters with mortality in pneumonia: Acute Phase Reactant Index is new index
- PMID: 40802406
- PMCID: PMC12341414
- DOI: 10.1590/1806-9282.20250005
Relationship between scoring systems and inflammatory parameters with mortality in pneumonia: Acute Phase Reactant Index is new index
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study is to investigate the relationship between risk scores and immune-inflammatory indices with prognosis and mortality in community-acquired pneumonia. Additionally, we aim to examine the association between mortality and the Acute Phase Reactant Index, which we developed using C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and albumin levels.
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted with 417 patients diagnosed with community-acquired pneumonia who presented to the emergency department of a tertiary care hospital between 2022 and 2023. The patients' demographic data, imaging findings, blood parameters, site of care, and 30-day mortality status were recorded. Risk scores, immune-inflammatory indices, and the Acute Phase Reactant Index were calculated. The risk scores and indices were compared with treatment outcomes and 30-day mortality results.
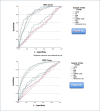
Results: In the receiver operating characteristic analysis, Acute Phase Reactant Index was found to be as effective as other risk scores in predicting mortality. Among them, Acute Phase Reactant Index had the highest area under the curve value. Additionally, in patients transferred from the ward to the ıntensive care unit, when the Acute Phase Reactant Index score cut-off value was set at 1.32, it accurately predicted mortality in 9 out of 13 patients (69.2%).
Conclusion: It was determined that Acute Phase Reactant Index is a better predictor of mortality than all other scores and inflammatory indices in community-acquired pneumonia. This suggests that the Acute Phase Reactant Index may be used as a prognostic factor in high-mortality lung diseases such as cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
The improved prediction value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio to pneumonia severity scores for mortality in the older people with community-acquired pneumonia.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):485. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-06121-2. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40604508 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
-
- Ramirez JA. Overview of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. UpToDate. 2024 Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-community-acquired-pneumon... .
-
- Erdem AB, Oğuztürk H, Tümer M, Işık B, Kayipmaz AE, Korkut S. Reliability of the Pneumonia Severity Score (PSI) Index in Patients Diagnosed with COVID-19 Pneumonia to Determine Outpatient Discharge. Signa Vitae. 2021;17(2):48–53. doi: 10.22514/sv.2020.16.0074. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

