Roles of hypoxia inducible factors in viral infection: Are they a potential therapeutic target?
- PMID: 40802588
- PMCID: PMC12351755
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2546680
Roles of hypoxia inducible factors in viral infection: Are they a potential therapeutic target?
Abstract
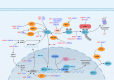
As a crucial nuclear transcription factor, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) serves essential functions in mediating cellular responses to hypoxic stress. Through oxygen-sensing mechanisms, HIF initiates downstream signaling cascades that coordinate metabolic reprogramming, immune modulation, and oncogenic progression in oxygen-deficient microenvironments. Current evidence positions HIF at the convergence of various pathologies, including microbial pathogenesis, carcinogenesis, and inflammatory disorders. This systematic review summarizes recent advances in HIF-mediated immunomodulation and virological mechanisms. The analysis emphasizes the fundamental importance of investigating HIF-related molecular pathways to address significant gaps in basic research.
Keywords: Hypoxia inducible factor; hypoxia; immunization; normoxia; virus infection.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Limning of HIF-2 and HIF-3 in the Tumor Microenvironment: Developing Concepts for the Treatment of Hypoxic Cancer.Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(5):513-521. doi: 10.2174/0115665240303179240427071748. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 38766832 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor in Glioblastoma Multiforme: a systematic review going beyond pathologic implications.Oncol Res. 2024 Jul 17;32(8):1239-1256. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.052130. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39055895 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Inducible Factor-2α (HIF-2α) Pathway Inhibitors.J Kidney Cancer VHL. 2025 Jul 2;12(3):1-15. doi: 10.15586/jkc.v12i3.413. eCollection 2025. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 2025. PMID: 40620865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Bidirectional Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 Alpha in Vascular Dementia Caused by Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):10398-10413. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04914-5. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40205304 Review.
-
A novel hypoxia-induced lncRNA, SZT2-AS1, boosts HCC progression by mediating HIF heterodimerization and histone trimethylation under a hypoxic microenvironment.Cell Death Differ. 2025 Apr;32(4):714-729. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01419-x. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Cell Death Differ. 2025. PMID: 39572656
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
