Deep learning reveals that multidimensional social status drives population variation in 11,875 US participant cohort
- PMID: 40802661
- PMCID: PMC12349134
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327729
Deep learning reveals that multidimensional social status drives population variation in 11,875 US participant cohort
Abstract
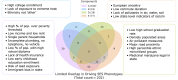
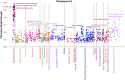
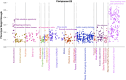
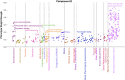
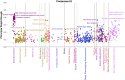
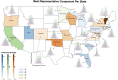
As an increasing realization, many behavioral relationships are interwoven with inherent variations in human populations. Presently, there is no clarity in the biomedical community on which sources of population variation are most dominant. The recent advent of population-scale cohorts like the Adolescent Brain Cognitive DevelopmentSM Study (ABCD Study®) are now offering unprecedented depth and width of phenotype profiling that potentially explains interfamily differences. Here, we leveraged a deep learning framework (conditional variational autoencoder) on the totality of the ABCD Study® phenome (8,902 candidate phenotypes in 11,875 participants) to identify and characterize major sources of population stratification. 80% of the top 5 sources of explanatory stratifications were driven by distinct combinations of 202 available socioeconomic status (SES) measures; each in conjunction with a unique set of non-overlapping social and environmental factors. Several sources of variation across this cohort flagged geographies marked by material poverty interlocked with mental health and behavioral correlates. Deprivation emerged in another top stratification in relation to urbanicity and its ties to immigrant and racial and ethnic minoritized groups. Conversely, two other major sources of population variation were both driven by indicators of privilege: one highlighted measures of access to educational opportunity and income tied to healthy home environments and good behavior, the other profiled individuals of European ancestry leading advantaged lifestyles in desirable neighborhoods in terms of location and air quality. Overall, the disclosed social stratifications underscore the importance of treating SES as a multidimensional construct and recognizing its ties into social determinants of health.
Copyright: © 2025 Marotta et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
DB is a shareholder and advisory board member at MindState Design Labs, USA. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
A New Measure of Quantified Social Health Is Associated With Levels of Discomfort, Capability, and Mental and General Health Among Patients Seeking Musculoskeletal Specialty Care.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Apr 1;483(4):647-663. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003394. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39915110
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Psychological interventions for adults who have sexually offended or are at risk of offending.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12(12):CD007507. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007507.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23235646 Free PMC article.
-
Racial and ethnic disparities in fecundability: a North American preconception cohort study.Hum Reprod. 2025 Jun 1;40(6):1183-1194. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaf067. Hum Reprod. 2025. PMID: 40246287
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

