N, N-dimethyltryptamine mitigates experimental stroke by stabilizing the blood-brain barrier and reducing neuroinflammation
- PMID: 40802766
- PMCID: PMC12346280
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adx5958
N, N-dimethyltryptamine mitigates experimental stroke by stabilizing the blood-brain barrier and reducing neuroinflammation
Abstract
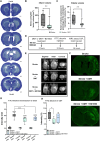
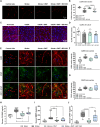
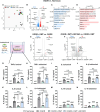
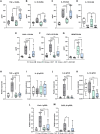
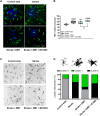
N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a psychoactive molecule present in the human brain. DMT is under clinical evaluation as a neuroprotective agent in poststroke recovery. Yet, its mechanism of action remains poorly understood. In a rat transient middle cerebral artery occlusion stroke model, we previously showed that DMT reduces infarct volume. Here, we demonstrate that this effect is accompanied by reduction of cerebral edema, attenuated astrocyte dysfunction, and a shift in serum protein composition toward an anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective state. DMT restored tight junction integrity and blood-brain barrier (BBB) function in vitro and in vivo. DMT suppressed the release of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in brain endothelial cells and peripheral immune cells and reduced microglial activation via the sigma-1 receptor. Our findings prove that DMT mitigates a poststroke effect by stabilizing the BBB and reducing neuroinflammation. Such interactions of DMT with the vascular and immune systems can be leveraged to complement current, insufficient, stroke therapy.
Figures


References
-
- Campbell B. C. V., De Silva D. A., Macleod M. R., Coutts S. B., Schwamm L. H., Davis S. M., Donnan G. A., Ischaemic stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 5, 70 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Pérez-Mato M., López-Arias E., Bugallo-Casal A., Correa-Paz C., Arias S., Rodríguez-Yáñez M., Santamaría-Cadavid M., Campos F., New perspectives in neuroprotection for ischemic stroke. Neuroscience 550, 30–42 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Goenka L., Uppugunduri Satyanarayana C. R., Kumar S. S., George M., Neuroprotective agents in acute ischemic stroke-A Reality Check. Biomed. Pharmacother. 109, 2539–2547 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

