Fasting-Induced Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Is Compromised In Anxa6-/- Mice
- PMID: 40802799
- PMCID: PMC12349248
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.70084
Fasting-Induced Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Is Compromised In Anxa6-/- Mice
Abstract
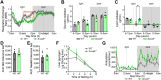
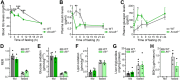
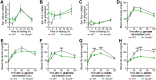
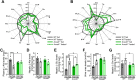
Maintaining constant blood glucose levels is essential for energizing glucose-dependent tissues. During the fed state, insulin lowers elevated blood glucose, while in the fasted state, glucagon maintains blood glucose levels through hepatic stimulation of fatty acid oxidation, glycogenolysis, and gluconeogenesis (GNG). The liver plays a crucial role in these metabolic adaptations. Deregulation of GNG is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), driven by hepatic insulin resistance, elevated glucagon levels, and excess circulating free fatty acids. The glucose metabolism of 8- to 12-week-old WT and Anxa6 knock-out (Anxa6-/-) mice was analysed during regular feeding and fasting using indirect calorimetry, tolerance tests and biochemical analysis. Despite normal insulin-sensitive control of glucose levels and effective glycogen mobilization, Anxa6-/- mice display rapid hypoglycaemia during fasting. This metabolic disarrangement, in particular during the early stages of fasting is characterized by a low respiratory exchange ratio (RER) and increased lipid oxidation during the diurnal period, indicating a reliance on lipid oxidation due to hypoglycaemia. Elevated glucagon levels during fasting suggest deficiencies in GNG. Further analysis reveals that Anxa6-/- mice are unable to utilize alanine for hepatic GNG, highlighting a specific impairment in the glucose-alanine cycle in fasted Anxa6-/- mice, underscoring the critical role of ANXA6 in maintaining glucose homeostasis under metabolic stress. During fasting, slightly reduced expression levels of alanine aminotransferase 2 (Gpt2) and lactate dehydrogenase (Ldha2), enzymes converting alanine to pyruvate, and the hepatic alanine transporter SNAT4 might contribute to these observations in the Anxa6-/- mice. These findings identify that ANXA6 deficiency causes an inability to maintain glycolytic metabolism under fasting conditions due to impaired alanine-dependent GNG.
Keywords: Annexin A6; SNAT; alanine; alanine‐dependent gluconeogenesis; hypoglycaemia.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular Physiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

