Polymerization and flanking domains of the bactofilin BacA collectively regulate stalk formation in Asticcacaulis biprosthecum
- PMID: 40802845
- PMCID: PMC12364344
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011542
Polymerization and flanking domains of the bactofilin BacA collectively regulate stalk formation in Asticcacaulis biprosthecum
Abstract
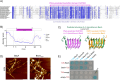
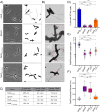
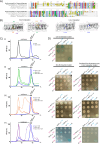
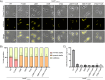
Bactofilins are a recently discovered class of cytoskeletal protein, widely implicated in subcellular organization and morphogenesis in bacteria and archaea. Several lines of evidence suggest that bactofilins polymerize into filaments using a central β-helical core domain, flanked by variable N- and C- terminal domains that may be important for scaffolding and other functions. In Asticcacaulis biprosthecum, the bactofilin BacA serves as a topological organizer of stalk synthesis, localizing to the stalk base and coordinating the synthesis of these long, thin extensions of the cell envelope. The easily distinguishable phenotypes of wild-type A. biprosthecum stalks and ΔbacA "pseudostalks" make this an ideal system for investigating how mutations in BacA affect its functions in morphogenesis. Here, we redefine the core domain of A. biprosthecum BacA using various bioinformatics and biochemical approaches to precisely delimit the N- and C- terminal domains. We then show that loss of these terminal domains leads to cells with severe morphological abnormalities, typically presenting a pseudostalk phenotype. BacA mutants lacking the N- and C- terminal domains also exhibit localization defects, implying that the terminal domains of BacA may be involved in its subcellular positioning, possibly through regulatory interactions with membrane-associated factors or other morphological proteins. We further show that point mutations that render BacA defective for polymerization lead to stalk synthesis defects. Overall, our study suggests that BacA's polymerization capacity and domain-mediated cellular positioning play a crucial role in the protein's function as a morphogenic regulator.
Copyright: © 2025 Jacq et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

