Euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis and its risk factors in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery: a single-centre nested case-control study in China
- PMID: 40803742
- PMCID: PMC12352176
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-098758
Euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis and its risk factors in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting surgery: a single-centre nested case-control study in China
Abstract
Objectives: This study examines the incidence and risk factors of euglycaemic diabetic ketoacidosis (euDKA) in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and evaluates their postoperative outcomes over a 6-month follow-up period.
Design: This study is a single-centre, nested case-control study, conducted in Tianjin, China.
Setting: An international cardiovascular hospital.
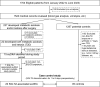
Participants: A total of 1524 patients, with a mean age of 64 (9) years, who underwent isolated elective CABG surgery were reviewed.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Data were extracted from electronic medical records. EuDKA cases were identified by reviewing laboratory examination results until discharge, including arterial blood gas analysis and urine samples. Logistic regression analysis was used in a case-control design to identify potential risk factors of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i)-associated euDKA. Post-discharge follow-up was conducted through regular outpatient visits.
Results: 15 patients with euDKA, all with type 2 diabetes, were identified post-surgery, 13 of whom were SGLT2i users. The cumulative incidence of euDKA within 7 days after surgery was 1% in the cohort, increasing to 7.6% among those who discontinued SGLT2i 1-6 days (n=171) before surgery. A case-control study added seven additional confirmed euDKA patients to the case group, resulting in 20 cases and 95 controls. Univariate regression analysis revealed that the risk of euDKA was 7.304 times higher (95% CI 2.517 to 21.197; p<0.001) for patients who took their last dose within 3 days prior to surgery compared with patients who discontinued SGLT2i 3-6 days before surgery. During the intraoperative period, pH <7.35 (OR: 7.017, 95% CI 1.849 to 26.638; p=0.004) and blood glucose <10 mmol L-1 (OR: 6.882, 95% CI 1.822 to 25.997; p=0.004) were associated with a higher risk of euDKA. Compared with controls, euDKA patients experienced a higher rate of type 5 myocardial infarction (6/20 (30%) vs 9/95 (9.5%); p=0.035) and recurrent ketosis post-discharge (3/19 (15.8%) vs 0/87 (0%); p=0.005).
Conclusions: This cohort study highlights a notable incidence of euDKA following CABG, particularly among patients using SGLT2i. Close monitoring in the ICU is recommended for patients with intraoperative abnormal blood glucose and pH levels to prevent euDKA.
Keywords: Adult intensive & critical care; Cardiac surgery; Case-Control Studies; Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2; EPIDEMIOLOGIC STUDIES; Risk Factors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preoperative SGLT2 Inhibitor Use and Postoperative Diabetic Ketoacidosis.JAMA Surg. 2025 Apr 1;160(4):423-430. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.7082. JAMA Surg. 2025. PMID: 39969891
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Postoperative Outcomes Among Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Users.JAMA Surg. 2025 Jun 1;160(6):681-689. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2025.0940. JAMA Surg. 2025. PMID: 40305034 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and inverse risk of new-onset atopic dermatitis in a cohort with diabetes: a nationwide active-comparator study.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jun 20;193(1):74-84. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf086. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40037684
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Systematic Review of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Related Risk Factors in the Primary Literature.Pharmacotherapy. 2017 Feb;37(2):187-194. doi: 10.1002/phar.1881. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Pharmacotherapy. 2017. PMID: 27931088
References
-
- Chinese Diabetes Society Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in china. Chin J Diabetes Mellitus. 2021;13:315–409.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
