Building a potent TREM2 agonistic, biparatopic, common light chain antibody
- PMID: 40803893
- PMCID: PMC12351705
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2025.2546554
Building a potent TREM2 agonistic, biparatopic, common light chain antibody
Abstract
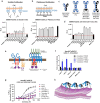
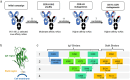
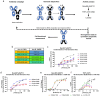
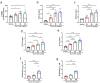
Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) plays an important role in microglial function and has been genetically linked to Alzheimer's disease. Activation of TREM2 signaling may contribute to protection against neurotoxic effects of amyloid. Numerous TREM2 activating antibodies have been shown to modulate downstream microglial functions to different degrees, with mixed results in preclinical models and in the clinic. We sought to generate an effectorless agonistic antibody that acted solely through TREM2 engagement with sufficient potency to activate TREM2 in the brain. Our approach focused on building a multivalent biparatopic TREM2 antibody that could mimic the higher order clustering induced by native polyanionic ligands of TREM2. We describe our screening strategy and findings that led to the discovery of a potential therapeutic molecule composed of antibodies selected for optimal affinity, binding epitopes, and geometry. The most productive antibody pair was selected from a common light chain yeast-display library, which required multiple rounds of affinity maturation. Lead antibody candidates were converted into asymmetric tetravalent bispecifics via controlled Fab-arm exchange and subsequently screened in signaling assays. The most productive antibody pair was reengineered into a symmetric tetravalent format, increasing potency and simplifying development. This molecule exhibited higher efficacy and potency in signaling assays than other antibody formats tested and elicited TREM2-mediated chemokine responses in vivo. Our results demonstrate a biparatopic strategy for producing a high potency TREM2 agonistic antibody with low effector function that can modulate TREM2 signaling in vitro and brain pharmacodynamic responses in vivo.
Keywords: Agonistic antibodies; Alzheimer’s disease; TREM2; biparatopic antibodies; bispecific antibodies; common light chain; microglia; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Biophysical mapping of TREM2-ligand interactions reveals shared surfaces for engagement of multiple Alzheimer's disease ligands.Mol Neurodegener. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00795-9. Mol Neurodegener. 2025. PMID: 39789647 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TREM2 on microglia cell surface binds to and forms functional binary complexes with heparan sulfate modified with 6-O-sulfation and iduronic acid.J Biol Chem. 2024 Sep;300(9):107691. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107691. Epub 2024 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39159814 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
