Extracellular vesicle-based drug overview: research landscape, quality control and nonclinical evaluation strategies
- PMID: 40804047
- PMCID: PMC12350758
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-025-02312-w
Extracellular vesicle-based drug overview: research landscape, quality control and nonclinical evaluation strategies
Abstract
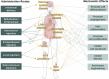
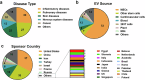
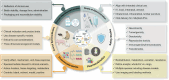
Extracellular vesicles share lipid‒protein membranes with their parent cells, allowing for the targeted transfer of bioactive cargo to recipient cells for functional modulation. The biological features allow extracellular vesicles to serve both as intrinsic therapeutics and as engineered delivery vehicles for targeted molecule transport. In recent years, extracellular vesicle-based therapy has shown great potential as a new therapeutic approach for traumatic conditions and degenerative, acute, and refractory diseases. As extracellular vesicle engineering continues to evolve, more innovative drugs are expected to receive investigational new drug approvals and marketing approvals from regulatory agencies in the future. However, many challenges exist in terms of mechanistic understanding, engineering modifications, manufacturing processes, quality control, and nonclinical research, and no drug regulatory authorities have currently issued specific technical evaluation guidelines for extracellular vesicle-based drugs, all of which have hindered the clinical translation of these drugs. In this article, which is focused primarily on extracellular vesicles derived from mammalian cells, we summarize the clinical translation and process development research status of extracellular vesicle-based drugs and propose both general considerations and key aspects of quality control strategies and nonclinical evaluations in the development process. The aim of this review is to provide valuable references for the development and evaluation of extracellular vesicle-based products, accelerate the clinical translation process, and benefit patients as soon as possible.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Dumontet, C. et al. Antibody-drug conjugates come of age in oncology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.22, 641–661 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Tsuchikama, K., Anami, Y., Ha, S. Y. Y. & Yamazaki, C. M. Exploring the next generation of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.21, 203–223 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Ginn, S. L. et al. Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide to 2023-an update. J. Gene Med26, e3721 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Bhagat, M. et al. Gene therapy: towards a new era of medicine. AAPS PharmSciTech26, 17 (2024). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

