Systemic immune-inflammation index and serum lactate dehydrogenase predict the prognosis of non-metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients receiving intensity-modulated radiotherapy
- PMID: 40804069
- PMCID: PMC12350786
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14455-5
Systemic immune-inflammation index and serum lactate dehydrogenase predict the prognosis of non-metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients receiving intensity-modulated radiotherapy
Abstract
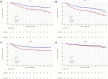
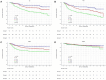
Increasing evidence indicates that the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are correlated with the prognosis of various malignancies. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of pre-treatment SII and LDH in patients with non-metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). We conducted a retrospective analysis of 756 patients with non-metastatic NPC. The optimal cut-off values for SII and LDH, determined using X-tile software, were 150 and 447, respectively. Independent prognostic factors for survival outcomes were identified using Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression analysis. Patients in the high SII group had significantly worse prognosis in 5-year OS (76.5 vs. 86.7%, p < 0.001), 5-year DMFS (77.3 vs. 85.4%, p < 0.001), and 5-year PFS (67.9 vs. 80.5%, p < 0.001) compared to the low SII group. Patients in the high LDH group had significantly worse prognosis in 5-year OS (72.1 vs. 85.0%, p < 0.001), 5-year DMFS (72.1 vs. 84.8%, p < 0.001), and 5-year PFS (63.7 vs. 77.7%, p < 0.001) compared to the low LDH group.Multivariate analysis showed that high SII and high LDH were significantly associated with poorer OS (p = 0.005 vs.p < 0.001), DMFS(p = 0.001 vs.p < 0.001), and PFS (p = 0.001 vs.p < 0.001). These results confirmed that both SII and LDH are independent prognostic factors for OS, DMFS, and PFS. In subgroup analysis, this predictive effect was more pronounced in locally advanced stages. Among patients with locally advanced NPC, the combination of SII and LDH showed the highest AUC values for predicting OS, DMFS, and PFS. Pre-treatment SII and LDH are important prognostic factors in patients with non-metastatic NPC. Furthermore, the combination of both provides a more accurate prognosis for patients with locally advanced NPC than either marker alone.
Keywords: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; Prognosis; Serum lactate dehydrogenase; Systemic immune-inflammation index.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J. Clin.71, 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Co, J., Mejia, M. B. & Dizon, J. M. Evidence on effectiveness of intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus 2-dimensional radiotherapy in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Meta-analysis and a systematic review of the literature. Head Neck. 38 (Suppl 1), E2130–2142 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Chen, Y. P. et al. Nasopharyng. Carcinoma Lancet394, 64–80 (2019).
-
- Schmidt, A. & Weber, O. F. In memoriam of Rudolf virchow: a historical retrospective including aspects of inflammation, infection and neoplasia. Contrib. Microbiol.13, 1–15 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Kou, J., Huang, J., Li, J., Wu, Z. & Ni, L. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis and responsiveness to immunotherapy in cancer patients: a systematic review and meta–analysis. Clin. Exp. Med.23, 3895–3905 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

