Coverage optimization of wireless sensor network utilizing an improved CS with multi-strategies
- PMID: 40804078
- PMCID: PMC12350845
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13247-1
Coverage optimization of wireless sensor network utilizing an improved CS with multi-strategies
Abstract
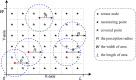
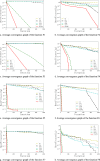
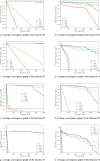
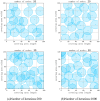
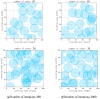
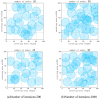
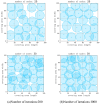
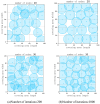
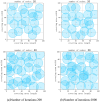
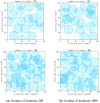
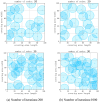
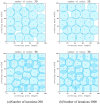
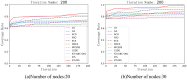
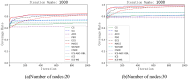
Coverage optimization in wireless sensor networks (WSNs) is critical due to two key challenges: (1) high deployment costs arising from redundant sensor placement to compensate for blind zones, and (2) ineffective coverage caused by uneven node distribution or environmental obstacles. Cuckoo Search (CS), as a type of Swarm Intelligence (SI) algorithm, has garnered significant attention from researchers due to its strong global search capability enabled by the Lévy flight mechanism. This makes it well-suited for solving such complex optimization problems. Based on this, this study proposes an improved Cuckoo Search algorithm with multi-strategies (ICS-MS), motivated by the 'no free lunch' theorem's implication that no single optimization strategy universally dominates. This is achieved by analyzing the standard CS through Markov chain theory, which helps identify areas for enhancement after characterizing the WSN and its coverage issues. Subsequently, the strategies that constitute ICS-MS are individually explained. The evaluation of the proposed ICS-MS is carried out in two phases. First, a numerical comparison is provided, a numerical comparison is presented by contrasting the performance of ICS-MS with the standard CS and its variations employing different strategies in terms of function optimization results. Second, a series of coverage optimization experiments are conducted under various scenarios. The experimental results demonstrate that ICS-MS exhibits significant improvements in both test function optimization and WSN coverage applications. In high-dimensional optimization problems, all enhancement strategies of ICS-MS prove independently effective, showing strong robustness, faster convergence speed, and higher solution accuracy. For WSN coverage optimization, the ICS-MS algorithm outperforms comparative algorithms. At 200 iterations, it achieves an average coverage increase of 2.32-22.17% for 20-node deployments and 2.75-22.21% for 30-node deployments. At 1000 iterations, coverage improves by 1.78-21.65% for 20-node deployments and 1.23-20.99% for 30-node deployments. Additionally, the algorithm demonstrates enhanced stability, more uniform node distribution, and reduced optimization randomness. These improvements collectively elevate coverage rates while lowering deployment costs.
Keywords: Coverage; Cuckoo search algorithm; Markov chain; Optimization; Wireless sensor network.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Augmented secretary bird optimization algorithm for wireless sensor network deployment and engineering problem.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 8;20(8):e0329705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329705. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40779557 Free PMC article.
-
Application of weighted centroid algorithm based on weight correction in node localization of wireless sensor networks.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23400. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08336-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40604197 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
-
- Javaid, S. et al. Self-powered sensors: Applications, challenges, and solutions. IEEE Sens. J.23(18), 20483–20509 (2023).
-
- Liu, X. et al. An approach for tool wear prediction using customized Densenet and GRU integrated model based on multi-sensor feature fusion. J. Intell. Manuf.34(2), 885–902 (2023).
-
- Yin, Y. et al. A 5G-enabled and self-powered sensor data management scheme for the smart medical platform system. IEEE Sens. J.23(18), 20904–20915 (2022).
-
- Maheshwari, A. & Chand, N. A survey on wireless sensor networks coverage problems[C]. in Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Communication, Computing and Networking: ICCCN 2018, NITTTR Chandigarh, India, 153–164. (Springer Singapore, 2019).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

