HNF4A ameliorates acute liver failure by inhibiting NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy
- PMID: 40804084
- PMCID: PMC12350633
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-13798-3
HNF4A ameliorates acute liver failure by inhibiting NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy
Abstract
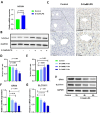
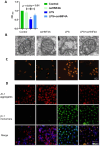
Intracellular iron homeostasis imbalance is linked to cellular ferroptosis and inflammatory injury diseases. NCOA4-mediated ferritin autophagy is vital for regulating intracellular iron homeostasis, but its impact on acute liver failure (ALF) pathogenesis and regulatory mechanisms remain unclear. This study explores the role and regulatory mechanisms of NCOA4 in hepatocyte ferroptosis and ALF progression. To investigate the relationship between NCOA4 expression and acute liver failure (ALF), we compared the protein expression levels in normal and pathological liver tissues. By establishing cell and mouse models, we determined the correlation among NCOA4 expression, ferroptosis, and inflammatory liver injury. Additionally, we explored the regulatory effect of NCOA4 on hepatocyte ferroptosis by interfering with gene expression and observing mitochondrial structure changes. Finally, we evaluated the regulation of NCOA4 expression and its protective effect against acute inflammatory injury in hepatocytes. Our results showed that NCOA4 expression was significantly higher in patients with hepatitis B virus - related acute - on - chronic liver failure (HBV - ACLF) compared to those with chronic hepatitis B. Similarly, NCOA4 was upregulated in ALF model mice and inflammatory hepatocytes. Silencing NCOA4 alleviated LPS - induced ferroptosis in inflammatory hepatocytes. Mechanistic research indicated that the transcription of hepatic nuclear factor 4 A (HNF4A) negatively regulated NCOA4. HNF4A transcriptionally inhibited NCOA4 expression, reducing hepatocyte ferroptosis through anti - ferritin autophagy. This study identified the HNF4A - NCOA4 axis and ferritinophagy as crucial factors in hepatocyte ferroptosis and the pathogenesis of acute liver failure (ALF). These findings suggest that the HNF4A - NCOA4 axis could be a potential therapeutic target for ALF.
Keywords: Acute liver failure; Ferroptosis; Hepatocyte; Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4A; Nuclear receptor coactivator 4.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations statement: The research in this paper adheres to the Declaration of Helsinki Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. Ethical approval: This study protocol was approved by the Medical ethics committee of the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University (2024-052-1). Informed consent: All patients obtained written informed consent.
Figures







Similar articles
-
KA-mediated excitotoxicity induces neuronal ferroptosis through activation of ferritinophagy.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Sep;30(9):e70054. doi: 10.1111/cns.70054. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39306799 Free PMC article.
-
Salidroside sensitizes Triple-negative breast cancer to ferroptosis by SCD1-mediated lipogenesis and NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy.J Adv Res. 2025 Aug;74:589-607. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.09.027. Epub 2024 Sep 29. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39353532 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2/UBE3B protects against acute lung injury by inhibiting ferritinophagy through the ubiquitination of NCOA4.Biol Direct. 2025 Jul 16;20(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13062-025-00678-z. Biol Direct. 2025. PMID: 40671136 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy in the ferroptosis of hepatocytes: A mechanistic viewpoint.Pathol Res Pract. 2025 Jun;270:155996. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2025.155996. Epub 2025 May 6. Pathol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40344841 Review.
-
The Crosstalk Between Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis in Ischemic Stroke: Regulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 20;45(1):73. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01593-7. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40684405 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

