Chondroitin sulfate protects against synaptic impairment caused by fluorosis through the Erk1/2-MMP-9 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40804089
- PMCID: PMC12350683
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14631-7
Chondroitin sulfate protects against synaptic impairment caused by fluorosis through the Erk1/2-MMP-9 signaling pathway
Abstract
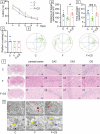
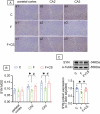
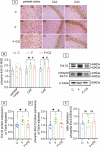
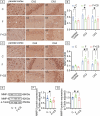
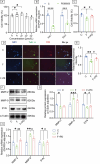
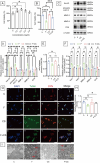
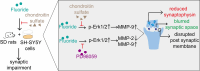
Prolonged exposure to fluoride may induce neurotoxic effects. Chondroitin sulfate (CS) exhibits protective functions within the central nervous system (CNS); however, the mechanism by which CS protects synapses against fluoride remains incompletely understood. Our objective was to investigate the protective efficacy of CS on synapses and decipher its underlying mechanisms. We showed that fluoride exposure reduced the expression of synaptic protein synaptophysin (SYN) and impaired learning and memory functions, whereas CS counteracted these alterations, suggesting its protective effect against fluoride-induced cognitive deficits. Further studies revealed disruption of the Erk1/2/MMP-2/MMP-9 signaling pathway both in vivo and in vitro, manifested by increased total Erk1/2, Erk1/2 phosphorylation and MMP-9 expression, along with decreased MMP-2 levels. Importantly, treatment of SH-SY5Y cells with PD98059 or CS attenuated fluoride-induced effects, indicating a regulatory role of CS in the Erk1/2/MMP-9 signaling pathway. However, MMP-2 was not implicated in this process. These data demonstrate the neuroprotective effects of CS and highlight its potential for protecting against fluoride-induced neurotoxicity and synaptic impairment.
Keywords: Chondroitin sulfate; Erk1/2; Fluoride; MMP-2; MMP-9; SYN.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. ARRIVE guidelines statement: Our study is reported in accordance with ARRIVE guidelines.
Figures
References
-
- Ottappilakkil, H., Babu, S., Balasubramanian, S., Manoharan, S. & Perumal, E. Fluoride induced neurobehavioral impairments in experimental animals: a brief review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res.201 (3), 1214–1236 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Zhao, Q. Y. et al. Effects of neuron autophagy induced by arsenic and fluoride on Spatial learning and memory in offspring rats. Chemosphere308 (Pt 2), 136341 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Zhao, Y. F., Zhao, X. J. & Wang, J. D. Choline alleviated perinatal fluoride exposure-induced learning and memory impairment through α4β2 nAChRs and α7 nAChRs in offspring mice. Environ. Toxicol.38 (3), 511–521 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Bartos, M. et al. Rat developmental fluoride exposure affects retention memory, leads to a depressive-like behavior, and induces biochemical changes in offspring rat brains. Neurotoxicology93, 222–232 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Ren, C., Li, H. H., Zhang, C. Y. & Song, X. C. Effects of chronic fluorosis on the brain. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf.244, 114021 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Grant number [Qian Education KY NO. [2021]183]/Guizhou Education Department Young Scientific and Technical Talents Project
- Grant number [82360672]/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant number 81960572 and 81260417/the China National Natural Science Foundation
- Grant number [Qiankehe Support 20192791]/Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Support Plan Project
- Key Laboratory of Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University(Cultivation) [2024] fy001/Pathology Morphology and Molecular Laboratory of the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

