Impact of two-dimensional dosimetric leaf gap on SRS-VMAT for single-isocenter multi-target brain metastases
- PMID: 40804092
- PMCID: PMC12350949
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14300-9
Impact of two-dimensional dosimetric leaf gap on SRS-VMAT for single-isocenter multi-target brain metastases
Abstract
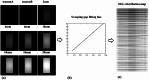
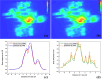
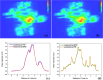
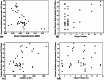
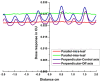
To explore the effects of two-dimensional dosimetric leaf gap (DLG) on the gamma pass rate (GPR) for single-isocenter multi-target (SIMT) stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. Two-dimensional DLG data were measured by an electronic portal imaging device (EPID) with the sweeping gap methods provided by Varian. A total of 56 arc fields from 28 SIMT patients were analyzed, including 19 with multiple targets and 9 with single targets. The leaf gap in patients' plan were modified using an in-house program, which adjusted the multileaf collimator positions based on the DLG values from the two-dimensional DLG distribution. Dose measurements were performed with EPID for both the original and modified plans. Comparisons were made between the measurements and the predicted dose planes from the treatment planning system using 3%/2 mm gamma criteria. Additionally, factors influencing the improvements in measurement results were analyzed.Compared to the original plan, the GPR for sweep test plans with leaf gaps of 2 mm, 4 mm, 6 mm, 10 mm, 14 mm, 16 mm and 20 mm increased by 12.2%, 17.6%, 25.4%, 58.2%, 83.6%, 84.3%, and 82%, respectively, after modification. For the clinical VMAT fields, GPR improvements fluctuated significantly due to the variations of modulation complexity score, the monitor units, as well as the number and volume of targets. The maximum GPR improvements with 16% and 36.3% were observed for the single-isocenter single-target and SIMT patients respectively. A linear relationship was found between GPR improvement and both modulation complexity score and the number of targets, whereas no significant correlation was found with monitor units or target volume. The two-dimensional DLG significantly impacts treatment plans for SIMT and single-isocenter single-target patients, particularly for SIMT cases. The GPR improvement correlates linearly with increases in modulation complexity score and the number of targets, while the monitor units and target volume show minimal correlation with GPR improvement. This study underscores the importance of accurate beam modeling as a key factor influencing GPR improvement.
Keywords: Dosimetric leaf gap; Electronic portal image device; Gamma pass rate; Multileaf collimators; Multiple target brain metastases; Sweep gap.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and informed consent: The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Shaanxi Provincial Cancer Hospital. All relative guidelines and regulations were followed in the methods. Due to the retrospective nature of the study, the Medical Ethics Committee of the Shaanxi Provincial Cancer Hospital waived the need for obtaining informed consent. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures
References
-
- Kraft, J. et al. Distance to isocenter is not associated with an increased risk for local failure in LINAC-based single-isocenter SRS or SRT for multiple brain metastases. Radiother. Oncol.159, 168–175 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Shaaer, A., Osei, E., Darko, J. & Gopaul, D. Dosimetric evaluation of VMAT treatment plans for patients with stage IIB or III non-small cell lung carcinomas. J. Radiother. Pract.22, e100 (2023).
-
- Han, Z. et al. Optimization of MLC parameters for TPS calculation and dosimetric verification: Application to single isocenter radiosurgery of multiple brain lesions using VMAT. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Exp.6(1), 015004 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

