Enhancing privacy in IoT-based healthcare using provable partitioned secure blockchain principle and encryption
- PMID: 40804099
- PMCID: PMC12350667
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14930-z
Enhancing privacy in IoT-based healthcare using provable partitioned secure blockchain principle and encryption
Abstract
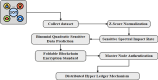
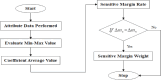
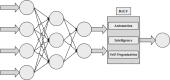
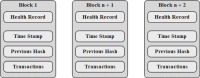
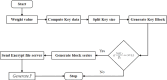
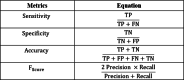
The Internet of Things (IoT) has attained significant interest recently, particularly in the medical field due to the quick development of IoT devices. Medical related data contains a significant volume of personal information, and it is crucial to maintain privacy. As medical information becomes increasingly electronic in the era of big data, securely and accurately storing medical information is critical. However, the heterogeneity of information systems poses a significant challenge to their sharing. Moreover, medical data typically comprises sensitive information, and sharing it can potentially lead to breaches of personal privacy. Data sharing is a significant concern in healthcare because of privacy leakage and security issues. To combat this issue, this paper introduces the prediction and Provable Partitioned Secure Block Chain Principle (PPSBCP) technique is used to secure healthcare data sharing. Initially, in the healthcare data analysis phase, the Preprocessing and normalization are carried out by Z-score normalized for analysing the healthcare-sensitive margins. The SSIR (Sensitive Spectral Impact Rate) method is applied to find the sensitive records. Based on the impact margins, the Binomial Quadratic Sensitive Data Prediction (BQSDP) method is applied to categorize the sensitive and non-sensitive information. In the blockchain phase, create a Hash Index Policy (HIP) to encrypt the data using a Foldable Blockchain Encryption Standard (FBES). The Master Node Handover Authentication Policy (MNHAP) is applied to verify the private key in the data safety. The Distributed Hyper Ledger Mechanism (DHLM) is applied to make the chain transaction principle. The proposed system accomplishes high performance in security by achieving the parameters in verification and validation as well as compared to the existing systems.
Keywords: Authentication policy; Blockchain; Data categorization; Data security; Hyper Ledger mechanism; Internet of Things; Partitioned secure blockchain principle; Privacy protection; Z-score normalization.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Azbeg, K., Ouchetto, O. & Andaloussi, S. J. BlockMedCare: A healthcare system based on IoT, blockchain and IPFS for data management security. Egypt. Inform. J.23(2), 329–343 (2022).
-
- Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Singh, R. P., Suman, R. & Rab, S. Blockchain technology applications in healthcare: An overview. Int. J. Intell. Netw.2, 130–139 (2021).
-
- Al-Rayani, B., Al-Harbi, J. & Al-Ghamdi, M. Enhancing security of IoT by using blockchain. Open Access Libr. J.9, 1–14 (2022).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

