Isolation and characterization of novel bacteriophages targeting Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
- PMID: 40804103
- PMCID: PMC12350841
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14811-5
Isolation and characterization of novel bacteriophages targeting Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Abstract
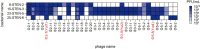
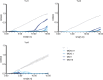
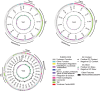
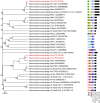
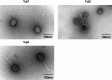
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is a bacterium often resistant to antibiotics and is a significant cause of nosocomial infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients. Phage therapy has shown promise as a potential treatment for such difficult-to-treat bacterial infections, but research on phages targeting this bacterium is very limited. In this study, we isolated 34 phages using four clinical strains of S. maltophilia and evaluated their infectivity and bactericidal activity. While some phages infected all four strains, many exhibited strain-specific infectivity. We investigated the bacterial growth curves in response to three phages, named Yut1, Yut2, and Yut4, and found that all phages exhibited potent lytic activity against the clinical strains even at low doses. Genome analysis found that the phages did not carry any lysogeny genes, virulence factors, or antibiotic resistance genes, suggesting their high potential as therapeutic phages. Furthermore, phylogenetic analysis suggested that Yut1 and Yut4 belong to a novel phage lineage. These results highlight the therapeutic potential of our novel phages to combat the growing antibiotic resistance problem.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

