Large language model powered knowledge graph construction for mental health exploration
- PMID: 40804250
- PMCID: PMC12350947
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62781-z
Large language model powered knowledge graph construction for mental health exploration
Abstract
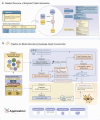
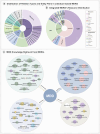
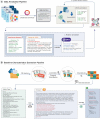
Mental health is a major global concern, yet findings remain fragmented across studies and databases, hindering integrative understanding and clinical translation. To address this gap, we present the Mental Disorders Knowledge Graph (MDKG)-a large-scale, contextualized knowledge graph built using large language models to unify evidence from biomedical literature and curated databases. MDKG comprises over 10 million relations, including nearly 1 million novel associations absent from existing resources. By structurally encoding contextual features such as conditionality, demographic factors, and co-occurring clinical attributes, the graph enables more nuanced interpretation and rapid expert validation, reducing evaluation time by up to 70%. Applied to predictive modeling in the UK Biobank, MDKG-enhanced representations yielded significant gains in predictive performance across multiple mental disorders. As a scalable and semantically enriched resource, MDKG offers a powerful foundation for accelerating psychiatric research and enabling interpretable, data-driven clinical insights.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
AI in Medical Questionnaires: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jun 23;27:e72398. doi: 10.2196/72398. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40549427 Free PMC article.
-
Menstrual Health Education Using a Specialized Large Language Model in India: Development and Evaluation Study of MenstLLaMA.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Jul 16;27:e71977. doi: 10.2196/71977. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40669074 Free PMC article.
-
UK paediatric speech and language therapists' perceptions on the use of telehealth in current and future clinical practice: An application of the APEASE criteria.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024 May-Jun;59(3):1163-1179. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12988. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2024. PMID: 38009588
-
MarkVCID cerebral small vessel consortium: I. Enrollment, clinical, fluid protocols.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Apr;17(4):704-715. doi: 10.1002/alz.12215. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 33480172 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- Vigo, D., Jones, L., Atun, R. & Thornicroft, G. The true global disease burden of mental illness: still elusive. Lancet Psychiatry9, 98–100 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Craske, M. G., Herzallah, M. M., Nusslock, R. & Patel, V. From neural circuits to communities: an integrative multidisciplinary roadmap for global mental health. Nat. Ment. Health1, 12–24 (2023).
-
- Derks, E. M., Thorp, J. G. & Gerring, Z. F. Ten challenges for clinical translation in psychiatric genetics. Nat. Genet.54, 1457–1465 (2022). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

