Study on constitutive model of marine soft soil based on disturbed state concept
- PMID: 40804275
- PMCID: PMC12350844
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15607-3
Study on constitutive model of marine soft soil based on disturbed state concept
Abstract
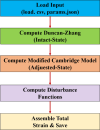
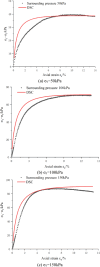
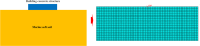
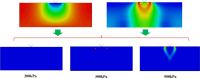
Marine soft soils are widely distributed in near-coastal areas and pose significant risks to the stability of structures due to their unique mechanical properties. While researchers worldwide have used various theoretical constitutive models and scientific methods to investigate the mechanical properties of marine soft soils, no attempts have been made to establish a mechanical model based on the concept of disturbed state for marine soft soils. In this paper, based on the concept of disturbed state, we utilize triaxial and creep test methods, apply the Duncan tensor modulus to describe the relatively complete state of marine soft soil, and modify the Cambridge model to characterize the fully adjusted state. Additionally, we derive the disturbance function to establish the intrinsic model for the disturbed state of marine soft soil. The model's accuracy is verified by comparing its predictions with experimental test results. Subsequently, the model is applied to engineering cases and compared with numerical simulation results. The study shows that the results from the disturbed state constitutive model are consistent with the experimental data and can effectively be used to assess the foundation bearing capacity of marine soft soil layers. The development of the constitutive model based on the concept of disturbed state offers a new theoretical framework and calculation method for studying the mechanical properties of marine soft soil in near-coastal regions.
Keywords: Constitutive model; Disturbed state concept; Geotechnical tests; Marine soft soil; Numerical calculation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
123I-MIBG scintigraphy and 18F-FDG-PET imaging for diagnosing neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 29;2015(9):CD009263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009263.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26417712 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jostad, H. P. & Yannie, J. A procedure for determining long-term creep rates of soft clays by triaxial testing. Eur. J. Environ. Civil Eng.26 (7), 2600–2615 (2022).
-
- LIN Dong. Constitutive model for compression behavior of marine silt soft clay and its application. Railway Constr. Technology, (10):1–5. (2023).
-
- Baojun, L. I., Weijun, H. U. A. N. G. & Pengjun, Z. H. A. N. G. Experimental study on cumulative plastic strain of marine soft soil under Cyclic loading. Mod. Tunn. Technol.57 (S1), 780–786 (2020).
-
- Qiangfei. Study on constitution model of loess based on disturbed state concept[D]. Doctoral Thesis of Chang’an University, (2016).
-
- Huang, M. S., Zou, S. H., Shi, Z. H. & Hong, Y. Constitutive modeling of cyclically loaded clays with entrapped gas bubbles under undrained and unexhausted conditions. Acta Geotech.18 (1), 265–278 (2023).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

