Multigene germline and somatic testing for epithelial ovarian cancer in China
- PMID: 40804290
- PMCID: PMC12350605
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-025-01074-6
Multigene germline and somatic testing for epithelial ovarian cancer in China
Abstract
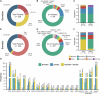
This study investigated BRCA1/2 and homologous recombination repair (HR) pathway gene variants in Chinese epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) patients. Germline and somatic variants in 21 HR-related genes were analyzed in 229 patients using a 21-gene ovarian panel and in 141 patients using a 508-gene pan-cancer panel. BRCA1, BRCA2, and HR-related gene mutation rates were 17.9%, 3.5%, and 23.1%, respectively, with TP53 as the most frequent somatic mutation (66.4%). Combined germline and somatic BRCA1/2 mutation rates rose to 23.6 and 6.1%. Survival analysis (n = 200) demonstrated longer overall survival (OS) in patients carrying BRCA1/2 or HR mutations. Notably, strategies including likely pathogenic (LP) and variants of uncertain significance (VUS) showed improved OS, especially in BRCA2 and BRCA1/2 somatic carriers. These findings suggest that integrating germline, somatic, and VUS data enhances survival prediction and guides treatment decisions in Chinese EOC patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sung, H. et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.71, 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Chen, W. et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin.66, 115–132 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D. & Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin.65, 5–29 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Zeng, H. et al. Cancer survival in China, 2003-2005: a population-based study. Int. J. Cancer136, 1921–1930 (2015). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2024-I2M-C&T-B-029/the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS)
- 2022-PUMCH-B-083, 2022-PUMCH-C-010, 2022-PUMCH-C-022 and 2022-PUMCH-D-003/the National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding
- 2025-I-ZD-001 and 2025-O-ZD-003/the Independent Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Complex, Severe and Rare Diseases in Peking Union Medical College Hospita
- Z220013/the Key Research Project of Beijing Natural Science Foundation
- UHB12577/Peking Union Medical College Hospital Talent Cultivation Program (Category D)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

