The augmentative role of chitosan and platelet-rich fibrin in reducing epidural fibrosis after laminectomy in rats
- PMID: 40804422
- PMCID: PMC12351833
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-025-02951-3
The augmentative role of chitosan and platelet-rich fibrin in reducing epidural fibrosis after laminectomy in rats
Abstract
Background: Epidural fibrosis (EF) is the major complication that develops in the operative region of the spinal vertebrae. This fibrous scar connects the connective tissue around the lateral nerve roots and epidural, resulting in severe pain post-spinal operation and impairment of the nerves' function.
Purpose: This study was conducted to investigate the effect of using platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), chitosan, and their combination in reducing epidural fibrosis after laminectomy in rats.
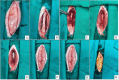
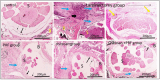
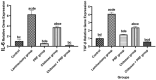
Methods: Ninety male Sprague Dawley rats weighing 255 ± 55 g were randomly assigned to five groups, each consisting of 15 rats: the normal group (control), the laminectomy group, the PRF group, the chitosan group, the combination group (PRF/chitosan), and the donor group. All rats, except the control group, had lumbar laminectomy surgeries between L3 and L5. Macroscopic analysis, histological evaluations, and mRNA analysis for TGFβ-1 and IL6 were compared statistically after a 30-day follow-up.
Results: In comparison to the laminectomy group, the EF area was significantly decreased in the PRF, chitosan, and combination groups. Histological study, macroscopic inspection, and mRNA expression of TGFβ-1 (P < 0.0001) and IL6 (P < 0.0001) show that the use of PRF with chitosan topically in dura following laminectomy resulted in a decrease in scar tissue formation, inflammation, and EF post-laminectomy.
Conclusion: The combination of chitosan with PRF is a potential therapeutic approach for minimizing EF in rats after laminectomy.
Keywords: Chitosan; Epidural fibrosis; Laminectomy; Platelets-rich fibrin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This research received no funding. This study adhered to the ethical standards and guidelines for the treatment and use of experimental animals as approved by the Ethical Committee, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Mansoura University, in accordance with the Ethics Committee of National Research Center-Egypt with registration number (Ph.D./102). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Kizilay Z, Kahraman Cetin N, Topcu A, İsmailoğlu Ö, Kurt Ömürlü İ, Aktas S, et al. Effect of etanercept on the formation of epidural fibrosis in an experimental model. Turk Neurosurg. 2018;28:111–7. - PubMed
-
- Wu C, Huang Y, Lee J, Tai T, Wu P, Jou I. Efficacy of topical cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogel in preventing post laminectomy/laminotomy fibrosis in a rat model. J Orthop Res. 2016;34:299–306. - PubMed
-
- Karatay M, Erdem Y, Koktekir E, Erkoc YS, Caydere M, Bayar MA. The effect of bevacizumab on spinal epidural fibrosis in a postlaminectomy rat model. Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22:753–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

