Influence of 2-hydroxyethylammonium acetate-based protic ionic liquids on the thermophysical properties of aqueous DL-alanine solutions
- PMID: 40804426
- PMCID: PMC12351930
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-025-01603-1
Influence of 2-hydroxyethylammonium acetate-based protic ionic liquids on the thermophysical properties of aqueous DL-alanine solutions
Abstract
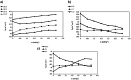
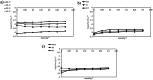
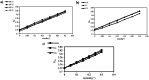
Understanding the hydration behavior of amino acids is fundamental to gaining insights into protein solvation mechanisms. Within this framework, examining the solvation properties of amino acids in aqueous media containing protic ionic liquids (PILs) a novel class of environmentally friendly solvents is crucial for characterizing their hydration dynamics. This research focuses on the influence of ammonium-based PILs, specifically mono-, bis-, and tris-(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium acetate, on the hydration characteristics of DL-alanine. By employing COSMO computational analysis alongside thermophysical property measurements, the study evaluates the hydration energies and σ-profiles of DL-alanine and the PILs. The thermophysical behavior of DL-alanine in aqueous solutions containing varying concentrations of protic ionic liquids (PILs) was systematically analyzed using experimental data and modeling approaches. The density, speed of sound, viscosity, and refractive index were measured for ternary solutions of DL-alanine, water, and PILs across a temperature range of (298.15 to 318.15) K under atmospheric pressure. The standard partial molar volume ([Formula: see text]) measured over the studied temperature range indicates that the solute-solvent interactions between [2-HEA]Ac and DL-alanine in the presence of water is 63.119 cm3·mol-1. Additionally, the hydration layer surrounding DL-alanine is notably influenced by temperature, as higher temperatures lead to the release of more water molecules relative to PIL-containing solutions. This temperature-dependent effect is especially pronounced in the presence of (2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium acetate, underscoring its significant impact on the hydration behavior of DL-alanine.
Keywords: DL-alanine; COSMO Analysis; Molar refractionon; Protic ionic liquids; Viscosity; Volumetric properties.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hydration behavior of L-proline in the presence of mono, bis, tris-(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium acetate protic ionic liquids: Thermophysical properties.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 8;14(1):27229. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77341-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39516508 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Electrophoresis.2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36251838 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Quality improvement strategies for diabetes care: Effects on outcomes for adults living with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 31;5(5):CD014513. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014513. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37254718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biological Water or Rather Water. in Biology?| The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01143. Accessed 28 Apr 2025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- (2024) Molecular Recognition Mediated by Hydrogen Bonding in Aqueous Media| Request PDF. ResearchGate. 10.1002/anie.202012315
-
- Water Dynamics in the Hydration Shells of Biomolecules| Chemical Reviews. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00765. Accessed 28 Apr 2025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Water is an. active matrix of life for cell and molecular biology. ResearchGate. 10.1073/pnas.1703781114
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
