Green synthesis and characterization of bioactive silver nanoparticles from Stachys tibetica
- PMID: 40804472
- PMCID: PMC12350943
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-92507-6
Green synthesis and characterization of bioactive silver nanoparticles from Stachys tibetica
Abstract
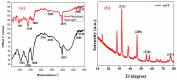
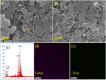
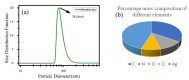
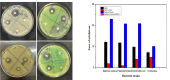
Stachys tibetica, a significant medicinal plant was collected from Ladakh (India) and subjected to extraction. The extract was titrated with AgNO3 at 50ºC to obtain silver nanoparticles with plant extract acts as a reducing and capping agent. The eco-friendly synthetic procedure utilizes the phytochemicals in Stachys tibetica, ensuring a sustainable and non-toxic approach to nanoparticle production. The characterization of the silver nanoparticles was conducted using various techniques, including Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and dynamic light scattering (DLS). Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) was utilized to examine the surface morphology, revealing the irregular and rugged spherical shape of the synthesized nanoparticles. Stachys tibetica-derived silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) act as a versatile and robust multifunctional material with proficient bioactivity and catalytic properties. The synthesized silver nanoparticles displayed effective antioxidant and antimicrobial properties against Bacillus Cereus, Pseudomonas, Escherichia coli, and S.Aureus. Additionally, the green nanoparticles degraded Rhodamine-B under sunlight irradiation within 1 h at a rate constant of 0.066 min- 1.
Keywords: Stachys Tibetica; FE-SEM; Rhodamine-b; Silver nanoparticles; XRD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles employing hamdard joshanda extract: putative antimicrobial potential against gram positive and gram negative bacteria.Biometals. 2024 Apr;37(2):389-403. doi: 10.1007/s10534-023-00556-z. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Biometals. 2024. PMID: 38055071
-
Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Asplenium dalhousiae and their potential biological properties.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 30;20(6):e0325533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325533. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40587502 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and assessment of antibacterial and antioxidant activities of silver nanoparticles utilizing Cassia occidentalis L. seed.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 27;14(1):7243. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57823-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38538702 Free PMC article.
-
Phytogenic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their roles in physiology and biochemistry of plants.Biometals. 2024 Feb;37(1):23-70. doi: 10.1007/s10534-023-00542-5. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Biometals. 2024. PMID: 37914858 Review.
-
An evidence-based environmental perspective of manufactured silver nanoparticle in syntheses and applications: a systematic review and critical appraisal of peer-reviewed scientific papers.Sci Total Environ. 2010 Feb 1;408(5):999-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.11.003. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Sci Total Environ. 2010. PMID: 19945151
References
-
- Fardood, S. T., Ramazani, A. & Moradi, S. Green synthesis of Ni–Cu–Mg ferrite nanoparticles using tragacanth gum and their use as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of polyhydroquinoline derivatives. J. Solgel Sci. Technol.82, 432–439 (2017).
-
- Albrecht, M. A., Evans, C. W. & Raston, C. L. Green chemistry and the health implications of nanoparticles. Green Chem.8, 417–432 (2006).
-
- Khaghani, S., Ghanbari, D. & Khaghani, S. Green synthesis of iron oxide-palladium nanocomposites by pepper extract and its application in removing of colored pollutants from water. J. Nanostruct.7, 175–182 (2017).
-
- Fardood, S. T., Atrak, K. & Ramazani, A. Green synthesis using tragacanth gum and characterization of Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite nanoparticles as a magnetically separable photocatalyst for organic dyes degradation from aqueous solution under visible light. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron.28, 10739–10746 (2017).
-
- Fardood, S. T., Ramazani, A. & Moradi, S. A novel green synthesis of nickel oxide nanoparticles using Arabic gum. Chem. J. Moldova, 115–118 (2017).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

