Muscle-building interventions improve glucose metabolism in elderly type 2 diabetic patients with sarcopenic obesity
- PMID: 40804678
- PMCID: PMC12344927
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-025-00993-2
Muscle-building interventions improve glucose metabolism in elderly type 2 diabetic patients with sarcopenic obesity
Abstract
Background: Among all the elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) of different body compositions, patients with sarcopenic obesity exhibited the most severe degree of insulin resistance despite possessing a normal body weight. It is well-established that interventions encompassing resistance training alone or in combination with whey protein supplementation, referred to hereafter as muscle-building interventions, are effective for increasing muscle mass and function in the elderly population. However, the impact of these muscle-building interventions on glucose metabolism in elderly T2DM patients with sarcopenic obesity remains unclear. The objective of this study was to elucidate the effect of muscle-building interventions on blood glucose and insulin resistance in elderly T2DM patients with sarcopenic obesity.
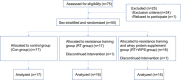
Methods: The muscle-building interventions in this study included resistance training alone and resistance training combined with whey protein supplementation. In this randomized controlled trial, elderly T2DM patients with sarcopenic obesity were divided into three distinct groups: the control group, the resistance training group, and the resistance training combined with whey protein supplement group. The muscle-building interventions were conducted for 12 weeks.
Results: Implementing muscle-building interventions showed significant improvements in glycemic indices (HbA1c, OGTT 2-hour plasma glucose) and insulin resistance levels (HOMA-IR, Gutt index) for elderly T2DM patients with sarcopenic obesity. These muscle-building interventions enhanced muscle functional indices (handgrip strength, 5-time chair stand test). The combination of resistance training with whey protein supplementation did not significantly enhance the favorable effects on glucose metabolism compared to resistance exercise alone. Correlation analyses revealed that improvements in muscle strength were significantly associated with enhancements in glucose metabolism.
Conclusions: In elderly T2DM patients with sarcopenic obesity, muscle-building interventions (particularly resistance exercise) have been shown to significantly improve blood glucose control and insulin resistance.
Keywords: Glucose metabolism; Insulin resistance; Muscle; Sarcopenic obesity; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Renji Hospital Ethics Committee (Approval No. LY2022-039-A). All participants provided written informed consent. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy: An Endocrine Society and European Society of Endocrinology Joint Clinical Practice Guideline.Eur J Endocrinol. 2025 Jun 30;193(1):G1-G48. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvaf116. Eur J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40652450
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy: An Endocrine Society and European Society of Endocrinology Joint Clinical Practice Guideline.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Aug 7;110(9):2405-2452. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaf288. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40652453 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB. Diabetes in asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009;301(20):2129–40. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner RN. Body composition in healthy aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;904:437–48. - PubMed
-
- Roubenoff R. Sarcopenic obesity: the confluence of two epidemics. Obes Res. 2004;12(6):887–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources