Regulatory roles of circular RNAs in Wnt and other oncogenic signaling pathways in breast cancer progression: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 40804731
- PMCID: PMC12351993
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-025-02967-9
Regulatory roles of circular RNAs in Wnt and other oncogenic signaling pathways in breast cancer progression: a comprehensive review
Abstract
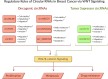
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are critical regulators in breast cancer (BC) progression, particularly through their interactions with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This comprehensive review elucidates the regulatory roles of key circRNAs, including circABCC4, circFAT1, circARL8B, and circDONSON, in modulating BC behavior. These circRNAs primarily function as microRNA sponges, influencing essential processes such as proliferation, metastasis, drug resistance, and cell survival. For instance, circDONSON promotes tumor growth and radioresistance through SOX4-mediated Wnt signaling, whereas circRNF10 exhibits tumor-suppressive properties. The dual role of circRNAs as oncogenes or tumor suppressors highlights their complexity. Their high stability and tissue-specific expression patterns position them as promising diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Dysregulation of circRNAs modulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling, a key driver of BC progression, promoting oncogenesis and therapeutic resistance. This review synthesizes evidence from peer-reviewed literature, emphasizing the molecular mechanisms and clinical implications of circRNA-Wnt interactions. By exploring these intricate networks, we identify novel opportunities for targeted BC therapies, underscoring the potential of circRNAs to transform diagnosis and treatment. Future research should prioritize standardizing circRNA quantification and validating findings across diverse patient cohorts to enhance clinical applicability.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CircularRNAs; Molecular agents; Wnt; Wnt signaling pathway; circRNA biogenesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors consent to publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring a circulating circRNA and miRNA biomarker panel for early detection of ovarian cancer through multiple omics analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25809. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11641-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670591 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs as novel biomarkers in triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Oct;49(10):9825-9840. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07502-1. Epub 2022 May 10. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35534586
-
Upregulation of CircCSPP1, CircNRIP1, and CircSMAD2 in Breast Cancer and Their Potential as Diagnostic Biomarkers.Iran Biomed J. 2025 May 1;29(3):159-166. doi: 10.61186/ibj.4945. Iran Biomed J. 2025. PMID: 40629030 Free PMC article.
-
SIAH2-AS1 stimulates breast cancer cell proliferation and migration via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21911. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06808-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595045 Free PMC article.
-
The function of circular RNAs in regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling: An innovative therapeutic strategy for breast and gynecological cancers.Pathol Res Pract. 2025 Jun;270:155944. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2025.155944. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40228402 Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2024 Jan 1;74(1). - PubMed
-
- Allison KH, Hammond MEH, Dowsett M, McKernin SE, Carey LA, Fitzgibbons PL, et al. Estrogen and progesterone receptor testing in breast cancer: ASCO/CAP guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(12):1346–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical