Prognostic Value of the De Ritis Ratio in Predicting Survival After Bladder Recurrence Following Nephroureterectomy for Upper Urinary Tract Tumors
- PMID: 40804804
- PMCID: PMC12346446
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15151840
Prognostic Value of the De Ritis Ratio in Predicting Survival After Bladder Recurrence Following Nephroureterectomy for Upper Urinary Tract Tumors
Abstract
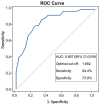
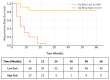
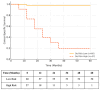
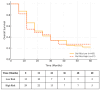
Background/Objectives: Upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) is often complicated by intravesical recurrence and cancer progression following radical nephroureterectomy (RNU). Identifying reliable prognostic biomarkers remains crucial for optimizing postoperative surveillance. The goal of this study was to assess the prognostic value of the De Ritis ratio (AST/ALT) in predicting bladder recurrence and oncologic outcomes in patients with clinically localized UTUC undergoing RNU. Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 87 patients treated with RNU between 2018 and 2025. Preoperative De Ritis ratios were calculated, and an optimal cut-off value of 1.682 was determined using ROC analysis. Recurrence-free survival (RFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), and overall survival (OS) were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression methods. Logistic regression was used to identify independent predictors of bladder recurrence. Results: A high De Ritis ratio was significantly associated with increased bladder recurrence and worse RFS and CSS, but not OS. Multivariate analysis confirmed that an elevated De Ritis ratio, current smoking, positive surgical margins, and synchronous bladder cancer were the independent predictors of bladder recurrence. The De Ritis ratio demonstrated strong discriminatory performance (AUC: 0.807), with good sensitivity and specificity for predicting recurrence. Conclusions: The De Ritis ratio is a simple, cost-effective preoperative biomarker that may aid in identifying UTUC patients at higher risk for intravesical recurrence and cancer-specific mortality. Incorporating this ratio into clinical decision-making could enhance risk stratification and guide tailored follow-up strategies.
Keywords: De Ritis ratio; intravesical recurrence; nephroureterectomy; prognostic biomarker; upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of a novel immune and nutritional score on prognosis in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma following radical nephroureterectomy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(12):10893-10909. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04977-8. Epub 2023 Jun 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37318591 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram based on geriatric nutritional risk index for predicting prognosis and postoperative complications in surgical patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(20):18185-18200. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05462-y. Epub 2023 Nov 30. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38032382 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term impact of synchronous and metachronous bladder cancer on prognosis after radical nephroureterectomy for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: results from a large population-based cohort in China.Int J Surg. 2025 Jul 3. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002892. Online ahead of print. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 40607984
-
Oncologic Outcomes of Kidney-sparing Surgery Versus Radical Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: A Systematic Review by the EAU Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Guidelines Panel.Eur Urol. 2016 Dec;70(6):1052-1068. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.07.014. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 27477528
-
Endoscopic intervention versus radical nephroureterectomy for the management of localized upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies.World J Urol. 2024 May 14;42(1):318. doi: 10.1007/s00345-024-05032-y. World J Urol. 2024. PMID: 38743260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soria F., Shariat S.F., Lerner S.P., Fritsche H.-M., Rink M., Kassouf W., Spiess P.E., Lotan Y., Ye D., Fernández M.I., et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis, preoperative evaluation and prognostic assessment of upper-tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) World J. Urol. 2016;35:379–387. doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1928-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rouprêt M., Babjuk M., Compérat E., Zigeuner R., Sylvester R.J., Burger M., Cowan N.C., Gontero P., Van Rhijn B.W.G., Mostafid A.H., et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: 2017 Update. Eur. Urol. 2018;73:111–122. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.07.036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moretto S., Piccolini A., Gallioli A., Contieri R., Buffi N., Lughezzani G., Breda A., Baboudjian M., van Rhijn B.W., Roupret M., et al. The role of intravesical chemotherapy following nephroureterectomy in upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2025;43:e1–e191. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2024.10.035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rouprêt M., Seisen T., Birtle A.J., Capoun O., Compérat E.M., Dominguez-Escrig J.L., Andersson I.G., Liedberg F., Mariappan P., Mostafid A.H., et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: 2023 Update. Eur. Urol. 2023;84:49–64. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.03.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Remzi M., Haitel A., Margulis V., Karakiewizc P., Montorsi F., Kikuchi E., Zigeuner R., Weizer A., Bolenz C., Bensalah K., et al. Tumour architecture is an independent predictor of outcomes after nephroureterectomy: A multi-institutional analysis of 1363 patients. BJU Int. 2009;103:307–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08003.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

