Rapid Identification of the SNP Mutation in the ABCD4 Gene and Its Association with Multi-Vertebrae Phenotypes in Ujimqin Sheep Using TaqMan-MGB Technology
- PMID: 40805073
- PMCID: PMC12345527
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15152284
Rapid Identification of the SNP Mutation in the ABCD4 Gene and Its Association with Multi-Vertebrae Phenotypes in Ujimqin Sheep Using TaqMan-MGB Technology
Abstract
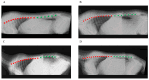
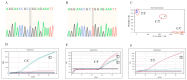
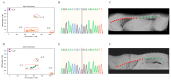
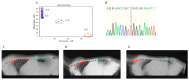
Ujimqin sheep, known for its distinctive multi-vertebrae phenotypes (T13L7, T14L6, and T14L7) and economic value, has garnered significant attention. However, conventional phenotypic detection methods suffer from low efficiency and high costs. In this study, based on a key SNP locus (ABCD4 gene, Chr7:89393414, C > T) identified through a genome-wide association study (GWAS), a TaqMan-MGB (minor groove binder) genotyping system was developed. the objective was to establish a high-throughput and efficient molecular marker-assisted selection (MAS) tool. Specific primers and dual fluorescent probes were designed to optimize the reaction system. Standard plasmids were adopted to validate genotyping accuracy. A total of 152 Ujimqin sheep were subjected to TaqMan-MGB genotyping, digital radiography (DR) imaging, and Sanger sequencing. the results showed complete concordance between TaqMan-MGB and Sanger sequencing, with an overall agreement rate of 83.6% with DR imaging. For individuals with T/T genotypes (127/139), the detection accuracy reached 91.4%. This method demonstrated high specificity, simplicity, and cost-efficiency, significantly reducing the time and financial burden associated with traditional imaging-based approaches. the findings indicate that the TaqMan-MGB technique can accurately identify the T/T genotype at the SNP site and its strong association with the multi-vertebrae phenotypes, offering an effective and reliable tool for molecular breeding of Ujimqin sheep.
Keywords: ABCD4 gene; TaqMan-MGB detection; Ujimqin sheep; molecular marker; multi-vertebrae; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Li C., Zhang X., Cao Y., Wei J., You S., Jiang Y., Cai K., Wumaier W., Guo D., Qi J., et al. Multi-vertebrae variation potentially contribute to carcass length and weight of Kazakh sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2017;150:8–10. doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2017.02.021. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

