Detection of Cathelicidin-1 and Cathelicidin-2 Biomolecules in the Milk of Goats and Their Use as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Mastitis
- PMID: 40805091
- PMCID: PMC12345514
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15152301
Detection of Cathelicidin-1 and Cathelicidin-2 Biomolecules in the Milk of Goats and Their Use as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Mastitis
Abstract
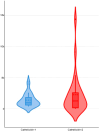
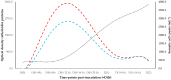
The objectives of the present work were as follows: (i) the detection of cathelicidin biomolecules in the milk of individual goats during the early stages of mastitis and their potential use for the diagnosis of mastitis at its early stage and (ii) the evaluation of the presence of cathelicidin proteins in the bulk-tank milk from goat and sheep farms. In an experimental study, after inoculation of Staphylococcus simulans into a mammary gland of goats, bacteriological and cytological examinations of milk samples, as well as proteomics examinations [two-dimensional gel electrophoresis analysis (2-DE) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometer (MALDI-TOF MS) analysis] were performed sequentially, from 4 to 48 h post-challenge. Cathelicidin-1 and cathelicidin-2 were detected consistently in milk samples obtained throughout the study, and spot optical densities obtained from PDQuest v.8.0 were recorded. Associations were calculated between the presence of mastitis in a mammary gland at a given timepoint and the detection of cathelicidin proteins in the respective milk sample. All inoculated mammary glands developed mastitis, confirmed by the consistent bacterial isolation from milk samples and the increased somatic cell content therein. Spot optical density of cathelicidin proteins was higher than in samples from contralateral mammary glands. There was a significant association between the presence of mastitis in a mammary gland and the detection of cathelicidin biomolecules in the respective milk sample; the overall accuracy was 81.8% (95% confidence interval: 70.4-90.2%). In a field investigation, the presence of cathelicidin proteins was evaluated in the bulk-tank milk of 32 dairy goat and 57 dairy sheep farms. In this part of the work, no cathelicidin proteins were detected in any bulk-tank milk sample of goat, 0.0% (95% confidence interval: 0.0-10.7%), or sheep, 0.0% (95% confidence interval: 0.0-6.3%), farms.
Keywords: biomarker; cathelicidin-1; cathelicidin-2; diagnosis; goat; mastitis; proteomics; sheep; somatic cell counts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of Cathelicidin-1 in the Milk as an Early Indicator of Mastitis in Ewes.Pathogens. 2019 Nov 28;8(4):270. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040270. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31795190 Free PMC article.
-
Milk proteins as mastitis markers in dairy ruminants - a systematic review.Vet Res Commun. 2022 Jun;46(2):329-351. doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-09901-y. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Vet Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 35195874 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Genetic diversity and molecular epidemiology of Streptococcus uberis in high-prevalence mastitis herds.J Dairy Sci. 2025 Jul 9:S0022-0302(25)00508-9. doi: 10.3168/jds.2025-26378. Online ahead of print. J Dairy Sci. 2025. PMID: 40645489
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addis M.F., Pisanu S., Marogna G., Cubeddu T., Pagnozzi D., Cacciotto C., Campesi F., Schianchi G., Rocca S., Uzzau S. Production and release of antimicrobial and immune defense proteins by mammary epithelial cells following Streptococcus uberis infection of sheep. Infect. Immun. 2013;81:3182–3197. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00291-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Katsafadou A.I., Tsangaris G.T., Anagnostopoulos A.K., Billinis C., Barbagianni M.S., Vasileiou N.G.C., Spanos S.A., Mavrogianni V.S., Fthenakis G.C. Differential quantitative proteomics study of experimental Mannheimia haemolytica mastitis in sheep. J. Proteom. 2019;205:103393. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2019.103393. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cubeddu T., Cacciotto C., Pisanu S., Tedde V., Alberti A., Pittau M., Dore S., Cannas A., Uzzau S., Rocca S., et al. Cathelicidin production and release by mammary epithelial cells during infectious mastitis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2017;189:66–70. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2017.06.002. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

