Treatment of KRAS-Mutated Pancreatic Cancer: New Hope for the Patients?
- PMID: 40805153
- PMCID: PMC12346701
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17152453
Treatment of KRAS-Mutated Pancreatic Cancer: New Hope for the Patients?
Abstract
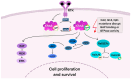
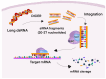
Pancreatic cancer, specifically pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), ranks among the most lethal malignancies, with a 5-year survival rate of under 10%. The most prevalent KRAS mutations occur in three hotspot residues: glycine-12 (G12), glycine-13 (G13), and glutamine-61 (Q61), leading to the constant activation of the Ras pathway, making them the primary focus in oncologic drug development. Selective KRAS G12C inhibitors (e.g., sotorasib, adagrasib) have demonstrated moderate efficacy in clinical trials; however, this mutation is infrequent in PDAC. Emerging therapies targeting KRAS G12D and G12V mutations, such as MRTX1133, PROTACs, and active-state inhibitors, show promise in preclinical studies. Pan-RAS inhibitors like ADT-007, RMC-9805, and RMC-6236 compounds provide broader coverage of mutations. Their efficacy and safety are currently being investigated in several clinical trials. A major challenge is the development of resistance mechanisms, including secondary mutations and pathway reactivation. Combination therapies targeting the RAS/MAPK axis, SHP2, mTOR, or SOS1 are under clinical investigation. Immunotherapy alone has demonstrated limited effectiveness, attributed to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, although synergistic effects are noted when paired with KRAS-targeted agents. Furthermore, KRAS mutations reprogram cancer metabolism, enhancing glycolysis, macropinocytosis, and autophagy, which are being explored therapeutically. RNA interference technologies have also shown potential in silencing mutant KRAS and reducing tumorigenicity. Future strategies should emphasize the combination of targeted therapies with metabolic or immunomodulatory agents to overcome resistance and enhance survival in KRAS-mutated PDAC.
Keywords: ADT-007; KRAS mutations; MRTX1133; RMC-6236; RMC-9805; RNAi; adagrasib; pan-RAS inhibitors; pancreatic cancer; sotorasib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ren S., Qian L.C., Cao Y.Y., Daniels M.J., Song L.N., Tian Y., Wang Z.Q. Computed tomography-based radiomics diagnostic approach for differential diagnosis between early- and late-stage pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024;16:1256–1267. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1256. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

