Scaffold-Free Functional Deconvolution Identifies Clinically Relevant Metastatic Melanoma EV Biomarkers
- PMID: 40805206
- PMCID: PMC12345765
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17152509
Scaffold-Free Functional Deconvolution Identifies Clinically Relevant Metastatic Melanoma EV Biomarkers
Abstract
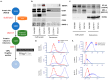
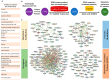
Background: Melanoma metastasis, driven by tumor microenvironment (TME)-mediated crosstalk facilitated by extracellular vesicles (EVs), remains a major therapeutic challenge. A critical barrier to clinical translation is the overlap in protein cargo between tumor-derived and healthy cell EVs. Objective: To address this, we developed Scaffold-free Functional Deconvolution (SFD), a novel computational approach that leverages a comprehensive healthy cell EV protein database to deconvolute non-oncogenic background signals. Methods: Beginning with 1915 proteins (identified by MS/MS analysis on an Orbitrap Fusion Lumos Mass Spectrometer using the IonStar workflow) from melanoma EVs isolated using REIUS, SFD applies four sequential filters: exclusion of normal melanocyte EV proteins, prioritization of metastasis-linked entries (HCMDB), refinement via melanocyte-specific databases, and validation against TCGA survival data. Results: This workflow identified 21 high-confidence targets implicated in metabolic-associated acidification, immune modulation, and oncogenesis, and were analyzed for reduced disease-free and overall survival. SFD's versatility was further demonstrated by surfaceome profiling, confirming enrichment of H7-B3 (CD276), ICAM1, and MIC-1 (GDF-15) in metastatic melanoma EV via Western blot and flow cytometry. Meta-analysis using Vesiclepedia and STRING categorized these targets into metabolic, immune, and oncogenic drivers, revealing a dense interaction network. Conclusions: Our results highlight SFD as a powerful tool for identifying clinically relevant biomarkers and therapeutic targets within melanoma EVs, with potential applications in drug development and personalized medicine.
Keywords: REIUS isolation; biomarker discovery; disease-free survival (DFS); extracellular vesicles (EV); melanoma; metastasis; overall survival (OS); proteomics; tumor microenvironment (TME).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors (S.S., S.B., X.W., E.K., M.F., M.K., C.L.A., F.Q., C.A., T.K., G.P., H.M., P.K., and M.S.E.) declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

