Balancing Innovation and Safety: Prediction, Prevention, and Management of Pneumonitis in Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Novel Anti-Cancer Agents
- PMID: 40805219
- PMCID: PMC12345867
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17152522
Balancing Innovation and Safety: Prediction, Prevention, and Management of Pneumonitis in Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Novel Anti-Cancer Agents
Abstract
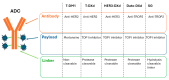
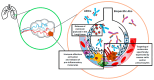
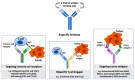
Pneumonitis is characterized as inflammation of the lung parenchyma, and a potential adverse effect of several anti-cancer therapies. Diagnosing pneumonitis can be particularly challenging in lung cancer patients due to inherent similarities in symptoms and radiological presentation associated with pneumonitis, as well as other common conditions such as infection or disease progression. Furthermore, many lung cancer patients have underlying pulmonary conditions that might render them more susceptible to severe or fatal outcomes from pneumonitis. Novel anti-cancer agents, such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and bispecific antibodies (BsAbs), are being incorporated into the treatment of lung cancer; therefore, understanding the risk and mechanisms underlying the potential development of pneumonitis with these new therapies is important to ensure continuous improvements in patient care. This narrative review provides an overview of the incidence of pneumonitis observed with novel anti-cancer agents, characterizes potential pathophysiological mechanisms underlying pneumonitis risk and emerging predictive biomarkers, highlights management strategies, and explores future directions for minimizing the risk of pneumonitis for lung cancer patients.
Keywords: antibody–drug conjugate; bispecific antibody; immunotherapy toxicity; lung cancer; pneumonitis.
Conflict of interest statement
S.G.: Honoraria: Amgen; Consulting/Advisory Role: GSK; Research Funding (institution): AstraZeneca, Merck. A.R.: Consulting/Advisory: Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Amgen, MSD; Y.L.: Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Amgen Consulting/Advisory: AstraZeneca, Pfizer Research Funding: AstraZeneca.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

