Research on the Adhesion Performance of Fast-Melting SBS-Modified Emulsified Asphalt-Aggregate Based on the Surface Free Energy Theory
- PMID: 40805401
- PMCID: PMC12348904
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18153523
Research on the Adhesion Performance of Fast-Melting SBS-Modified Emulsified Asphalt-Aggregate Based on the Surface Free Energy Theory
Abstract
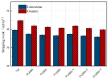
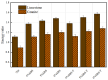
Aiming at the problems of complex process flow, high energy consumption, and difficult emulsification in the preparation of traditional SBS-modified emulsified asphalt, a preparation method of fast-melting SBS (referred to as SBS-T) modified emulsified asphalt based on the integration of modification and emulsification is proposed. Based on surface free energy theory, the contact angles between three rapid-melting SBS-modified emulsified asphalts with different dosages and three probe liquids (deionized water, glycerol, and formamide) were measured using the sessile drop method. The adhesion performance of the asphalt-aggregate system was studied by means of micromechanical methods. The evaluation indicators such as the cohesion work of the emulsified asphalt, the adhesion work of asphalt-aggregate, the spalling work, and the energy ratio were analyzed. The results show that the SBS-T modifier can significantly improve the thermodynamic properties of emulsified asphalt. With increasing modifier content, the SBS-T-modified emulsified asphalt demonstrated enhanced cohesive work, improved asphalt-aggregate adhesive work, and increased energy ratio, while showing reduced stripping work. At equivalent dosage levels, the SBS-T-modified emulsified asphalt demonstrates a slight improvement in adhesion performance to aggregates compared to conventional SBS-modified emulsified asphalt. The SBS-T emulsified modified asphalt provides an effective technical solution for the preventive maintenance of asphalt pavements.
Keywords: adhesion performance; fast-melting SBS; modified emulsified asphalt; surface free energy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

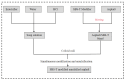

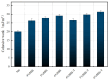
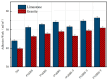
References
-
- Chompoorat T., Likitlersuang S. Influence of asphalt binder on time-temperature shift function for asphalt concrete at large strains. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2016;20:2765–2774. doi: 10.1007/s12205-016-0665-4. - DOI
-
- Xiao J., Jiang W., Ye W., Shan J., Wang Z. Effect of cement and emulsified asphalt contents on the performance of cement-emulsified asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019;220:577–586. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.051. - DOI
-
- Motamed A., Salomon D., Sakib N., Bhasin A. Emulsified asphalt residue recovery and characterization: Combined use of moisture analyzer balance and dynamic shear rheometer. Transp. Res. Rec. 2014;2444:88–96. doi: 10.3141/2444-10. - DOI
-
- Islam R., Ashani S., Wasiuddin N. Effects of curing time, temperature, and vacuum pressure on asphalt emulsion residue recovered by vacuum drying method. J. Test. Eval. 2015;43:1134–1145. doi: 10.1520/JTE20140014. - DOI
-
- Abedini M., Hassani A., Kaymanesh M., Yousefi A.A. The rheological properties of a bitumen emulsion modified with two types of SBR latex. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2016;34:1589–1594. doi: 10.1080/10916466.2016.1214600. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

