Assessment of Low-Dose rhBMP-2 and Vacuum Plasma Treatments on Titanium Implants for Osseointegration and Bone Regeneration
- PMID: 40805462
- PMCID: PMC12348453
- DOI: 10.3390/ma18153582
Assessment of Low-Dose rhBMP-2 and Vacuum Plasma Treatments on Titanium Implants for Osseointegration and Bone Regeneration
Abstract
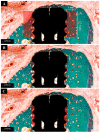
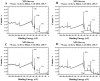
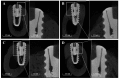
This study evaluated the effects of low-dose recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) coating in combination with vacuum plasma treatment on titanium implants, aiming to enhance osseointegration and bone regeneration while minimizing the adverse effects associated with high-dose rhBMP-2. In vitro analyses demonstrated that plasma treatment increased surface energy, promoting cell adhesion and proliferation. Additionally, it facilitated sustained rhBMP-2 release by enhancing protein binding to the implant surface. In vivo experiments using the four-beagle mandibular defect model were conducted with the following four groups: un-treated implants, rhBMP-2-coated implants, plasma-treated implants, and implants treated with both rhBMP-2 and plasma. Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and medical CT analyses revealed a significantly greater volume of newly formed bone in the combined treatment group (p < 0.05). Histological evaluation further confirmed superior outcomes in the combined group, showing significantly higher bone-to-implant contact (BIC), new bone area (NBA), and inter-thread bone density (ITBD) compared to the other groups (p < 0.05). These findings indicate that vacuum plasma treatment enhances the biological efficacy of low-dose rhBMP-2, representing a promising strategy to improve implant integration in compromised conditions. Further studies are warranted to determine the optimal clinical dosage.
Keywords: bone regeneration; osseointegration; rhBMP-2; titanium implant; vacuum plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





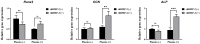



Similar articles
-
Development of Dual-Functional Titanium Implant for Osseointegration and Antimicrobial Effects via Plasma Modification.Int Dent J. 2025 Aug 28;75(6):103871. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2025.103871. Online ahead of print. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 40882320 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Local Drug and Chemical Compound Delivery on Bone Regeneration Around Dental Implants in Animal Models: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018 Jan/Feb;33(1):e1-e18. doi: 10.11607/jomi.6333. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018. PMID: 29340346
-
Effect of Secondary Non-Thermal Plasma Decontamination on Ethanol-Treated Endosteal Implant Surfaces: An In Vivo Study of Osseointegration.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2025 Aug;113(8):e35628. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.35628. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40742223
-
The Effect of Three-Dimensional Stabilization Thread Design on Biomechanical Fixation and Osseointegration in Type IV Bone.Biomimetics (Basel). 2025 Jun 12;10(6):395. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics10060395. Biomimetics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40558364 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Micro-computed Tomography in Dental Implant Osseointegration: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Acad Radiol. 2025 Feb;32(2):1086-1099. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.09.011. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39368915
References
-
- Brunette D.M., Tengvall P., Textor M., Thomsen P., Textor M., Sittig C., Brunette D.M. Titanium in Medicine: Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2001. Properties and biological significance of natural oxide films on titanium and its alloys; pp. 171–230.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

