Discovery of Hub Genes Involved in Seed Development and Lipid Biosynthesis in Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Using UID Transcriptome Sequencing
- PMID: 40805785
- PMCID: PMC12349325
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14152436
Discovery of Hub Genes Involved in Seed Development and Lipid Biosynthesis in Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Using UID Transcriptome Sequencing
Abstract
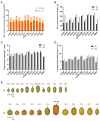
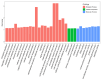
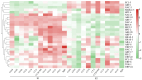
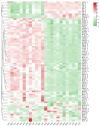
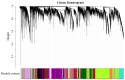
Sea buckthorn is a vital woody oil species valued for its role in soil conservation and its bioactive seed oil, which is rich in unsaturated fatty acids and other compounds. However, low seed oil content and small seed size are the main bottlenecks restricting the development and utilization of sea buckthorn. In this study, we tested the seed oil content and seed size of 12 sea buckthorn cultivars and identified the key genes and transcription factors involved in seed development and lipid biosynthesis via the integration of UID RNA-seq (Unique Identifiers, UID), WGCNA (weighted gene co-expression network analysis) and qRT-PCR (quantitative real-time PCR) analysis. The results revealed five cultivars (CY02, CY11, CY201309, CY18, CY21) with significantly higher oil contents and five cultivars (CY10, CY201309, CY18, CY21, CY27) with significantly heavier seeds. A total of 10,873 genes were significantly differentially expressed between the S1 and S2 seed developmental stages of the 12 cultivars. WGCNA was used to identify five modules related to seed oil content and seed weight/size, and 417 candidate genes were screened from these modules. Among them, multiple hub genes and transcription factors were identified; for instance, ATP synthase, ATP synthase subunit D and Acyl carrier protein 1 were related to seed development; plastid-lipid-associated protein, acyltransferase-like protein, and glycerol-3-phosphate 2-O-acyltransferase 6 were involved in lipid biosynthesis; and transcription factors DOF1.2, BHLH137 and ERF4 were associated with seed enlargement and development. These findings provide crucial insights into the genetic regulation of seed traits in sea buckthorn, offering targets for future breeding efforts aimed at improving oil yield and quality.
Keywords: Hippophae rhamnoides L.; UID RNA-seq; WGCNA; lipid biosynthesis; seed development; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The genome of Hippophae salicifolia provides new insights into the sexual differentiation of sea buckthorn.Gigascience. 2025 Jan 6;14:giaf046. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaf046. Gigascience. 2025. PMID: 40601420 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition Analysis of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae) in Georgia and Development of Innovative Valorization Technologies.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 14;13(7):e70507. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70507. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40661806 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective study of vaginal topical pretreatment of compound sea-buckthorn oil suppository in postmenopausal women prior to colposcopy.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 26;15(1):10364. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95036-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40133564 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) on factors related to metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial.Phytother Res. 2022 Nov;36(11):4101-4114. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7596. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 36043374
-
Ear drops for the removal of ear wax.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 25;7(7):CD012171. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012171.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30043448 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mei D., Ma X., Fu F., Cao F. Research Status and Development Prospects of Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Resources in China. Forests. 2023;14:2461. doi: 10.3390/f14122461. - DOI
-
- Yang B., Kalimo K.O., Tahvonen R.L., Mattila L.M., Katajisto J.K., Kallio H.P. Effect of dietary supplementation with sea buckthorn (Hippophaë rhamnoides) seed and pulp oils on the fatty acid composition of skin glycerophospholipids of patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2000;11:338–340. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2863(00)00088-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gutiérrez L.-F., Belkacemi K. Palmitoleic Acid Enrichment of Seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Pulp Oil by Crystallization Process. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008;43:2003–2022. doi: 10.1080/01496390802064091. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 32261133521; 23-46-00026/International (Regional) Collaborative Research Project of NSFC-RSF
- 32071799/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32111540255/International (Regional) Cooperation and Exchange Project of NSFC-NRF
- 2023JH2/10700016/International Cooperation Plan Project of Liaoning Province
- 2025-kj-020/Project of Sea buckthorn Development and Management Center of the Ministry of Water Re-sources
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

