Water Stress Promotes Secondary Sexual Dimorphism in Ecophysiological Traits of Papaya Seedlings
- PMID: 40805796
- PMCID: PMC12349495
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14152445
Water Stress Promotes Secondary Sexual Dimorphism in Ecophysiological Traits of Papaya Seedlings
Abstract
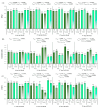
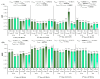
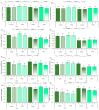
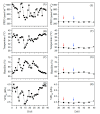
Plant genders could express different functional strategies to compensate for different reproductive costs, as females have an additional role in fruit and seed production. Secondary sexual dimorphism (SSD) expression is frequently greater under stress than under optimal growth conditions. The early gender identification in papaya may help to reduce orchard costs because the most desirable fruit shape is formed by hermaphrodite plants. We hypothesized that (a) gender ecophysiological phenotyping can be an alternative to make gender segregations in papaya seedlings, and (b) such gender segregation will be more efficient after a short drought exposure than under adequate water conditions. To test such hypotheses, seedlings of two papaya varieties ('Candy' and 'THB') were exposed to two kind of treatments: (1) water shortage (WS) for 45 h, after which they were well watered, and (2) continuously well-watered (WW). Study assessed the ecophysiological responses, such as stomatal conductance (gs), SPAD index, optical reflectance indices, morphological traits, and biomass accumulation in females (F) and hermaphrodites (H). In WS treatment, the SSD was expressed in 14 of 18 traits investigated, while in WW treatment, the SSD was expressed only in 7 of 18 traits. As tools for SSD expression, gs and simple ratio pigment index (SRPI) must be measured on the first or second day after the imposed WS was interrupted, respectively, while the other parameters must be measured after a period of four days. In some traits, the SSD was expressed in only one variety, or the response of H and F plants were of opposite values for two varieties. The choice of the clearest responses of gender segregation in WS treatment will be greenness index, combination of normalized difference vegetation index (CNDVI), photochemical reflectance index (PRI), water band index (WBI), SRPI, leaf number, leaf dry mass, and leaf mass ratio. If the WW conditions are maintained for papaya seedling production, the recommendation in gender segregation will be the analysis of CNDVI, carotenoid reflectance index 2 (CRI2), WBI, and SRPI. The non-destructive optical leaf indices segregated papaya hermaphrodites from females under both water conditions and eventually could be adjusted for wide-scale platform evaluations, with planned space arrangements of seedlings, and sensor's set.
Keywords: Carica papaya L.; SPAD; SSD; biomass; gender segregation; morphology; optical leaf properties; stomatal conductance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Antiseptics for burns.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 12;7(7):CD011821. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011821.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28700086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campostrini E., Glenn D.M. Ecophysiology of papaya: A Review. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2007;19:413–424. doi: 10.1590/S1677-04202007000400010. - DOI
-
- de Oliveira E.J., Amorim V.B.O., Matos E.L.S., Costa J.L., da Silva Castellen M., Pádua J.G., Dantas J.L.L. Polymorphism of microsatellite markers in papaya (Carica papaya L.) Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010;28:519–530. doi: 10.1007/s11105-010-0180-6. - DOI
-
- De Luca Y., Cozzolino S., Cristaudo A., Widmer A., Cafasso D. Early sex identification by leaflet distance in plantlets of Cycas revoluta. Euphytica. 2024;220:150. doi: 10.1007/s10681-024-03407-1. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

