HIV Infection in Portugal: Measuring the Time Between Linkage to Care and Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation
- PMID: 40805844
- PMCID: PMC12346046
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13151812
HIV Infection in Portugal: Measuring the Time Between Linkage to Care and Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation
Abstract
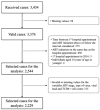
Background/Objectives: The timely initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) in persons living with HIV (PLWH) can improve clinical outcomes. However, ART commencement is often delayed. Portugal, despite having one of the highest new HIV diagnosis rates within the European Union, has limited available national-level data. Prior evidence from 2017 to 2018 suggests that the average time to ART initiation exceeds the recommendations for optimal patient benefits. This study aimed to determine the number of days from the first hospital appointment to the commencement of ART among newly diagnosed PLWH in Portugal between 2017 and 2022 at the national level and across different hospitals. It was hypothesized that newly diagnosed PLWH in Portugal experience a delay in ART initiation beyond the recommended timeframe. Methods: A retrospective analysis of records from Portuguese public tertiary care hospitals, which manage most HIV patients, was conducted. Descriptive statistics (measures of central tendency, dispersion, and frequency) were applied, along with association tests and a binary logistic regression model to examine factors influencing the timing of ART initiation. Results: A total of 2229 cases (out of 3434 received) from 19 hospitals were considered eligible. The median time interval between the first hospital appointment and ART initiation was 29.00 days, with a decreasing tendency between 2017 and 2022. Patients initiating therapy after 14 days had higher CD4 levels and lower viral loads compared to those starting within 14 days, with statistical significance. Conclusions: Continuous and regular monitoring of key indicators, such as the time to ART initiation, is pivotal for assessing the effectiveness of HIV treatment programs and pinpointing areas in need of improvement.
Keywords: clinical care continuum; people living with HIV; rapid ART initiation; retrospective analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hammer S.M., Squires K.E., Hughes M.D., Grimes J.M., Demeter L.M., Currier J.S., Eron J.J., Feinberg J.E., Balfour H.H., Deyton L.R., et al. A Controlled Trial of Two Nucleoside Analogues plus Indinavir in Persons with Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection and CD4 Cell Counts of 200 per Cubic Millimetre or Less. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;337:725–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199709113371101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrade H.B., Shinotsuka C.R., Da Silva I.R.F., Donini C.S., Li H.Y., De Carvalho F.B., Alvarenga Americano do Brasil P.E., Bozza F.A., Japiassu A.M. Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy for Critically Ill HIV Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0186968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186968. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials