Prevalence and Impact of Antidepressant and Anti-Anxiety Use Among Saudi Medical Students: A National Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 40805887
- PMCID: PMC12346393
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13151854
Prevalence and Impact of Antidepressant and Anti-Anxiety Use Among Saudi Medical Students: A National Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
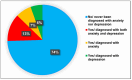
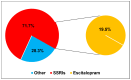
Background: Mental health issues among medical students have gained increasing attention globally, with studies indicating a high prevalence of psychological disorders within this population. The use of antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications has become a common response to these mental health challenges. However, it is crucial to understand the extent of their usage and associated effects on students' mental health and academic performance. This cross-sectional study explored the use of antidepressants and anti-anxiety drugs and their impact on the mental health of medical students in Saudi Arabia. Methods: A cross-sectional survey of 561 medical students from 34 universities was conducted between March and July 2024. An anonymous online questionnaire was used to collect sociodemographic, mental health, and medication usage-related information. Results: Most of the participants were female (71.5%) and aged 21-25 years (62.7%). Approximately 23.8% of them used antidepressants, 5.6% reported using anti-anxiety medications, and 14.0% used both types of medication. Among the medication users, 71.7% were using selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and 28.3% were using other medications. Adverse drug reactions were reported by 58.8% of the participants, and 39.6% changed drugs with inadequate efficacy. Notably, 49.0% of the respondents who have ever used medications discontinued their medication without consulting a healthcare professional. Despite these challenges, 62.0% of the participants felt that their medications had a positive impact on their academic performance, 73.4% believed that the benefits outweighed the drawbacks, and 76.2% expressed a willingness to continue taking their medication. In particular, 77.6% agreed that treatment with these drugs could prevent mental breakdowns. Sleep duration, physical activity, and family history of psychiatric disorders were significantly associated with medication use, with p values of 0.002, 0.014, and 0.042, respectively. Conclusions: These results shed light on the need to understand the prescribing practices of antidepressant and anti-anxiety drugs among medical students while promoting the appropriate use of these medications among the students. There is a need to incorporate mental health interventions into counseling services and awareness programs to support students. Future longitudinal studies are needed to explore long-term trends.
Keywords: anti-anxiety medications; antidepressants; medical students; mental well-being.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rotenstein L.S., Ramos M.A., Torre M., Segal J.B., Peluso M.J., Guille C., Sen S., Mata D.A. Prevalence of depression, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation among medical students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016;316:2214–2236. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.17324. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brenneisen Mayer F., Souza Santos I., Silveira P.S., Itaqui Lopes M.H., de Souza A.R.N.D., Campos E.P., de Abreu B.A.L., Hoffman I., II, Magalhães C.R., Lima M.C.P. Factors associated to depression and anxiety in medical students: A multicenter study. BMC Med. Educ. 2016;16:282. doi: 10.1186/s12909-016-0791-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources