Impact of Maternal Overweight and Obesity on Pregnancy Outcomes Following Cesarean Delivery: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 40805926
- PMCID: PMC12346095
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13151893
Impact of Maternal Overweight and Obesity on Pregnancy Outcomes Following Cesarean Delivery: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
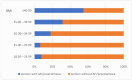
Background/Objectives: Maternal overweight and obesity are critical factors increasing the risk of various pregnancy complications. Maternal obesity can lead to fetal macrosomia and a heightened risk of intrauterine death, with long-term implications for the child's health. This study aimed to analyze the incidence of obesity and its impact on pregnancy outcomes in women who delivered by cesarean section at the University Hospital "St. George", Plovdiv. Methods: A single-center retrospective cohort study was conducted. The documentary method was used for gathering data. Records were randomly selected. The statistical methods used included mean values, confidence intervals (of mean), frequency, and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality of distribution. Data comparisons were performed using the Mann-Whitney test. Mean values of numerical variables were compared using the independent samples t-test. Results: In total, 46.36% of women in this study were affected by obesity to varying degrees, and the proportion of women who were overweight at the end of their pregnancy was 37.85%. In the studied cohort, 15.99% of women were affected by hypertensive complications. This significant prevalence of obesity highlights concerns regarding body weight among women of reproductive age. This study emphasized a strong correlation between maternal obesity, particularly severe obesity, and the occurrence of preeclampsia. Conclusions: In this study among women who delivered by cesarean section, a significant proportion of them were affected by overweight and obesity. Data for our country are insufficient, and a more in-depth study of this problem is needed. Future research should explore the long-term impacts of maternal obesity on the health of the mother and the newborn.
Keywords: cesarean section; complications; hypertensive disorders; maternal obesity; pregnancy outcome; pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal and neonatal outcomes of elective induction of labor.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009 Mar;(176):1-257. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2009. PMID: 19408970 Free PMC article.
-
Planned early delivery versus expectant management for hypertensive disorders from 34 weeks gestation to term.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 15;1(1):CD009273. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009273.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28106904 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Incentives for increasing prenatal care use by women in order to improve maternal and neonatal outcomes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 15;2015(12):CD009916. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009916.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26671418 Free PMC article.
-
Different intensities of glycaemic control for women with gestational diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 7;4(4):CD011624. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011624.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 10;10:CD011624. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011624.pub3. PMID: 27055233 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Tabacu M.C., Istrate-Ofiţeru A.M., Manolea M.M., Dijmărescu A.L., Rotaru L.T., Boldeanu M.V., Şerbănescu M.S., Tudor A., Novac M.B. Maternal obesity and placental pathology in correlation with adverse pregnancy outcome. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2022;63:99–104. doi: 10.47162/RJME.63.1.09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Spasova Z. Obesity and climate change—The new global syndemic. Bulg. J. Public Health. 2025;17:91–102.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources