The Role of Square Dancing in Psychological Capital: Evidence from a Large Cross-Sequential Study
- PMID: 40805943
- PMCID: PMC12345902
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare13151913
The Role of Square Dancing in Psychological Capital: Evidence from a Large Cross-Sequential Study
Abstract
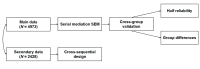
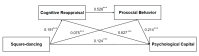
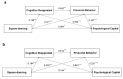
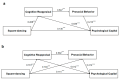
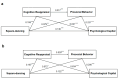
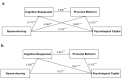
(1) Background: Rapid population aging in China intensifies physical and mental health challenges, including negative emotions and social barriers. Physical activity (PA) fosters resilience, adaptability, and successful aging through emotional and social benefits. This study examines the relationship between square-dancing exercise and psychological capital (PsyCap) in middle-aged and elderly individuals using cross-validation, subgroup analysis, and a cross-sequential design. (2) Methods: A cross-sectional study with 5714 participants employed a serial mediation model. Online questionnaires assessed square-dancing exercise, cognitive reappraisal, prosocial behavior tendencies, PsyCap, and interpersonal relationships. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 27.0 and Mplus 8.3, incorporating correlation analysis, structural equation modeling, and subgroup comparisons. (3) Results: (a) Cognitive reappraisal and prosocial behavior mediated the link between square-dancing and PsyCap through three pathways; (b) model stability was confirmed across two random subsamples; (c) cross-group differences emerged in age and interpersonal relationships. Compared with secondary data, this study further validated PsyCap's stability over six months post-pandemic. (4) Conclusions: The study, based on China's largest square-dancing sample, establishes a robust serial mediation model. The findings strengthen theoretical foundations for PA-based interventions promoting psychological resilience in aging populations, highlighting structured exercise's role in mental and social well-being.
Keywords: cognitive reappraisal; cross-sequential study; middle-aged and older adults; prosocial behavior tendency; psychological capital (PsyCap); square-dancing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation and analysis of mental health status of the older adult in western rural areas.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 16;13:1612600. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1612600. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40740371 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Square Dance Interventions on Physical and Mental Health among Chinese Older Adults: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 19;19(10):6181. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19106181. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35627716 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of interpersonal relationships on college students' physical activity: chain-mediated effects of social support and exercise motivation.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 18;16:1567122. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1567122. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40606875 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

