Obtaining and Characterization of Nutraceuticals Based on Linoleic Acid Derivatives Obtained by Green Synthesis and Their Valorization in the Food Industry
- PMID: 40806004
- PMCID: PMC12348337
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17152416
Obtaining and Characterization of Nutraceuticals Based on Linoleic Acid Derivatives Obtained by Green Synthesis and Their Valorization in the Food Industry
Abstract
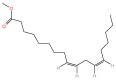
Background/Objectives: As an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid, linoleic acid (LA) plays an important role in maintaining the integrity of cellular membranes, modulating inflammatory responses, and mediating intracellular signaling. This review explores the structure, properties, and nutritional significance of LA and its bioactive derivatives, with particular attention to sustainable production methods and their potential applications. Methods: A comprehensive review of the recent literature was conducted, emphasizing the use of green synthesis techniques, such as enzyme-catalyzed biocatalysis and microbiological transformations, in order to obtain LA-derived nutraceuticals. Analyses were conducted on the key aspects related to food industry applications, regulatory frameworks, and emerging market trends. Results: Through green synthesis strategies, LA derivatives with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties have been developed. There is potential for these compounds to be incorporated into health-oriented food products. In spite of this, challenges remain regarding their stability and bioavailability. Furthermore, there are inconsistencies in international regulatory standards which prevent these compounds from being widely adopted. Conclusions: The development of functional and sustainable food products based on linoleic acid derivatives obtained using ecological methods offers significant potential. Research is required to optimize production processes, enhance compound stability, and clinically validate health effects. The integration of the market and the safety of consumers will be supported by addressing regulatory harmonization.
Keywords: food industry; green synthesis; linoleic acid; nutraceuticals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Interventions to improve safe and effective medicines use by consumers: an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD007768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007768.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24777444 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Alam M.S., Maity M.K., Nazmi A.S., Ali M. Anthocyanins: Pharmacology and Nutraceutical Importance. Bentham Science Publishers Pvt. Ltd.; Sharjah, United Arab Emirates: 2024. Anthocyanins: Pharmacology and Nutraceutical Importance; pp. 92–107. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization . Noncommunicable Diseases Country Profiles 2018. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018. pp. 1–223.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

