Advances in Nanotechnology Research in Food Production, Nutrition, and Health
- PMID: 40806027
- PMCID: PMC12348174
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17152443
Advances in Nanotechnology Research in Food Production, Nutrition, and Health
Abstract
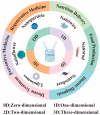
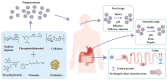
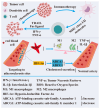
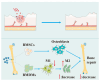
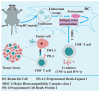
Nanotechnology, as a burgeoning interdisciplinary field, has a significant application potential in food nutrition and human health due to its distinctive structural characteristics and surface effects. This paper methodically examines the recent advancements in nanotechnology pertaining to food production, functional nutrition delivery, and health intervention. In food manufacturing, nanoparticles have markedly enhanced food safety and quality stability via technologies such as antimicrobial packaging, intelligent sensing, and processing optimization. Nutritional science has used nanocarrier-based delivery systems, like liposomes, nanoemulsions, and biopolymer particles, to make active substances easier for the body to access and target. Nanotechnology offers innovative approaches for chronic illness prevention and individualized treatment in health interventions by enabling accurate nutritional delivery and functional regulation. Nonetheless, the use of nanotechnology encounters hurdles, including safety evaluations and regulatory concerns that require additional investigation. Future research should concentrate on refining the preparation process of nanomaterials, conducting comprehensive examinations of their metabolic mechanisms within the human body, and enhancing pertinent safety standards to facilitate the sustainable advancement of nanotechnology in food production, nutrition, and health.
Keywords: food production; human health; nanotechnology; nutritional delivery; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Emerging trends of biomedical nanotechnology in nutrition, health monitoring and disease diagnosis.3 Biotech. 2025 Jun;15(6):152. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04291-9. Epub 2025 May 5. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40336812 Review.
-
Commercial utilization of bacteriocins: tackling challenges and exploring their potential as alternatives to antibiotics.Future Microbiol. 2025 Jul;20(10):681-693. doi: 10.1080/17460913.2025.2520693. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Future Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40536428 Review.
-
Ophthalmia Neonatorum.2025 Jul 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31855399 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Pandit K.H., Patil P.B., Goswami A.D., Pinjari D.V. Handbook of Green and Sustainable Nanotechnology: Fundamentals, Developments and Applications. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2022. Fabrications from renewable sources and agricultural wastes and characterization strategies of green nanomaterials; pp. 1–15.
-
- Paradva K.C., Jangir R., Kalla S. Green nanomaterials: Synthesis and applications in wastewater treatment. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023;158:111584. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111584. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

