Unveiling Adulteration in Herbal Markets: MassARRAY iPLEX Assay for Accurate Identification of Plumbago indica L
- PMID: 40806300
- PMCID: PMC12346827
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157168
Unveiling Adulteration in Herbal Markets: MassARRAY iPLEX Assay for Accurate Identification of Plumbago indica L
Abstract
The root of Plumbago indica L. is commercially available in herbal markets in both crude and powdered forms. P. indica root is a key ingredient in numerous polyherbal formulations. However, P. indica has two closely related species, P. zeylanica L. and P. auriculata Lam. Since only P. indica is traditionally used in Thai polyherbal products, adulteration with other species could potentially compromise the therapeutic efficacy and overall effectiveness of these formulations. To address this issue, a MassARRAY iPLEX assay was developed to accurately identify and differentiate P. indica from its closely related species. Five single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites-positions 18, 112, 577, 623, and 652-within the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region were selected as genetic markers for species identification. The assay demonstrated high accuracy in identifying P. indica and was capable of detecting the species at DNA concentrations as low as 0.01 ng/µL. Additionally, the assay successfully identified P. zeylanica in commercial crude drug samples, highlighting potential instances of adulteration. Furthermore, it was able to distinguish P. indica in mixed samples containing P. indica, along with either P. zeylanica or P. auriculata. The developed MassARRAY iPLEX assay proves to be a reliable and effective molecular tool for authenticating P. indica raw materials. Its application holds significant potential for ensuring the integrity of herbal products by preventing misidentification and adulteration.
Keywords: DNA barcode; MassARRAY; Plumbago; identification; leadwort; raw material; single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

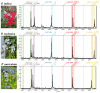
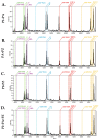

References
-
- Abdu A., Prakash A., Kondal R., Sharma S., Bhagat M., Pal R., Singh H., Singh B., Kaur S. Comprehensive review on Plumbago indica: Traditional, pharmacological insights and conservation strategies. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2024;14:1–16. doi: 10.7324/JAPS.2024.200049. - DOI
-
- Thitiorul S., Ratanavalachai T., Tanuchit S., Itharat A., Sakpakdeejaroen I. Genotoxicity and interference with cell cycle activities by an ethanolic extract from Thai Plumbago indica roots in human lymphocytes in vitro. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013;14:2487–2490. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.4.2487. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Makchuchit S., Rattarom R., Itharat A. The anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory effects of Benjakul extract (a Thai traditional medicine), its constituent plants and its some pure constituents using in vitro experiments. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017;89:1018–1026. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.066. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duenngai K., Promraksa B., Janthamala S., Thanee M., Sirithawat P., Wisungre S., Deechan S., Meechai N., Paratang P., Techasen A. Antioxidant and Anticancer Potentials and Metabolic Profiling of Benjakul, A Thai Herbal Preparation. Trop. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024;8:6877–6883. doi: 10.26538/tjnpr/v8i4.18. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

