Redox-Epigenetic Crosstalk in Plant Stress Responses: The Roles of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in Modulating Chromatin Dynamics
- PMID: 40806301
- PMCID: PMC12345703
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26157167
Redox-Epigenetic Crosstalk in Plant Stress Responses: The Roles of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in Modulating Chromatin Dynamics
Abstract
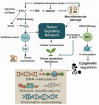
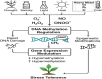
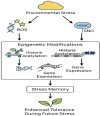
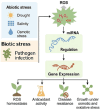
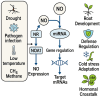
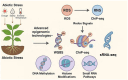
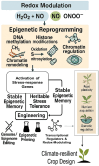
Plants are constantly exposed to environmental stressors such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures, which threaten their growth and productivity. To counter these challenges, they employ complex molecular defense systems, including epigenetic modifications that regulate gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence. This review comprehensively examines the emerging roles of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) as central signaling molecules orchestrating epigenetic changes in response to abiotic stress. In addition, biotic factors such as pathogen infection and microbial interactions are considered for their ability to trigger ROS/RNS generation and epigenetic remodeling. It explores how ROS and RNS influence DNA methylation, histone modifications, and small RNA pathways, thereby modulating chromatin structure and stress-responsive gene expression. Mechanistic insights into redox-mediated regulation of DNA methyltransferases, histone acetyltransferases, and microRNA expression are discussed in the context of plant stress resilience. The review also highlights cutting-edge epigenomic technologies such as whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS), chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq), and small RNA sequencing, which are enabling precise mapping of stress-induced epigenetic landscapes. By integrating redox biology with epigenetics, this work provides a novel framework for engineering climate-resilient crops through the targeted manipulation of stress-responsive epigenomic signatures.
Keywords: chromatin dynamics; crop improvement; epigenomic analysis; gene regulation; molecular signaling; stress adaptation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic alterations in prostate cancer: the role of chromatin remodeling.Epigenomics. 2025 Jul 22:1-25. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2025.2535938. Online ahead of print. Epigenomics. 2025. PMID: 40694614 Review.
-
Redox-signalling and Redox Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Health and Disease.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2025;23(2):99-111. doi: 10.2174/0118715257282030240130095754. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38549520 Review.
-
[Epigenetics' implication in autism spectrum disorders: A review].Encephale. 2017 Aug;43(4):374-381. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.07.007. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Encephale. 2017. PMID: 27692350 French.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Epigenetics in evolution and adaptation to environmental challenges: pathways for disease prevention and treatment.Epigenomics. 2025 Apr;17(5):317-333. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2025.2464529. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Epigenomics. 2025. PMID: 39948759 Review.
References
-
- Gupta P., Seth C.S. 24-Epibrassinolide regulates functional components of nitric oxide signalling and antioxidant defense pathways to alleviate salinity stress in Brassica juncea L. cv. Varuna. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023;42:4207–4222. doi: 10.1007/s00344-022-10884-y. - DOI
-
- Jahan U., Kafeel U., Khan F.A., Jahan A. Reactive nitrogen species in plants. In: Yousuf P.Y., Shabir P.A., Hakeem K.R., editors. Advances in Plant Nitrogen Metabolism. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2022. pp. 203–212. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

